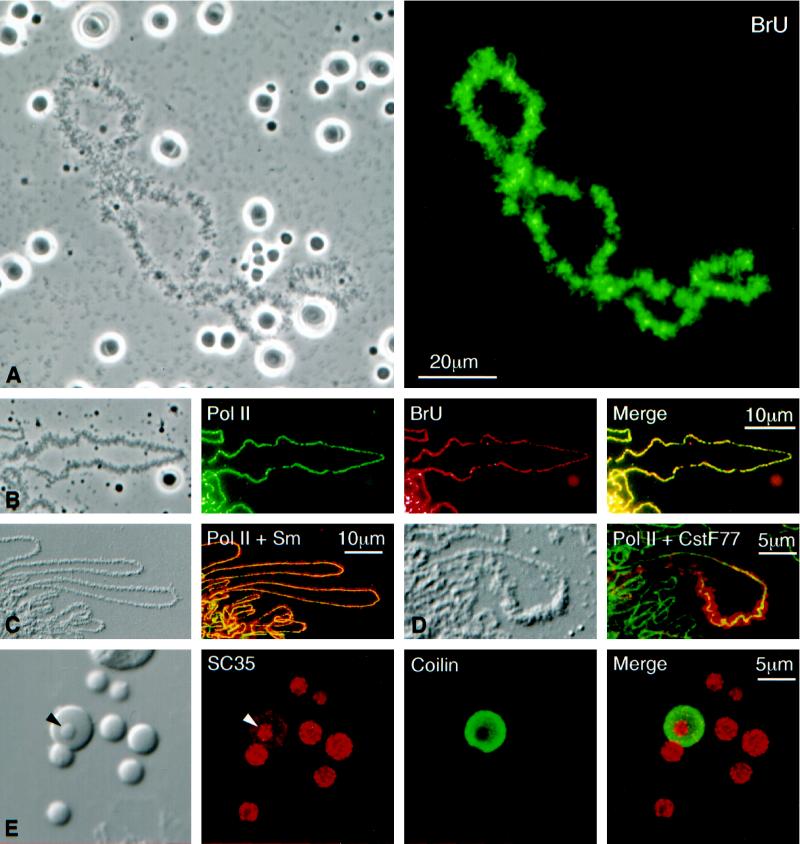
Figure 2.
(A) Phase-contrast (left) and fluorescent (right) images of a single lampbrush chromosome with scattered nucleoli, Cajal bodies, and B-snurposomes from a spread preparation of a Xenopus GV. The oocyte had been injected 4.5 h earlier with 20 mM BrUTP (253 ng in 23 nl). Strong BrU label in the lampbrush chromosome U loops is revealed by immunostaining with an anti-BrU antibody (right). Nucleoli are weakly stained, but Cajal bodies and B-snurposomes are completely negative. (B) Single loop from a lampbrush chromosome of the newt Notophthalmus. The oocyte had been injected 1 h earlier with 20 mM BrUTP (253 ng in 23 nl). The left panel shows a phase-contrast image of the loop. The following three panels show staining of the loop axis with an antibody against pol II (mAb H5, green), BrU incorporation (red), and a merge of the two images. Pol II and newly transcribed RNA are precisely colocalized. (C) Differential interference contrast (DIC) and immunofluorescence images of loops from a Notophthalmus lampbrush chromosome after double staining for pol II (mAb H14, green) and the Sm epitope (mAb Y12, red). Pol II occurs only along the axis, whereas splicing snRNPs are present throughout the RNP matrix of the loop. (D) Loop from a Notophthalmus lampbrush chromosome after double staining for pol II (mAb H14, green) and the 77-kDa subunitof the cleavage stimulation factor CstF (red). CstF77 occurs through the matrix of a single “thin-to-thick” transcription unit. (E) The left panel shows the DIC image of a single Cajal body with an attached B-snurposome and an internal B-like inclusion (arrowhead). Nearby are six free B-snurposomes. The following three panels show the same field after staining for the SR protein SC35 (red), the Cajal body marker coilin (green), and a merge of the two images. The B-snurposomes and the inclusion stain strongly for SC35; coilin is limited to the matrix of the Cajal body, which also stains weakly for SC35.