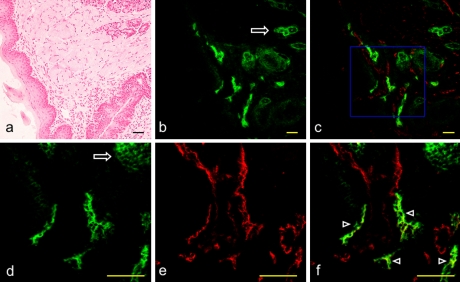
Fig. 1.
Expression of PECAM-1 and podoplanin on the mouse lingual lymphatic vessels. (a) H-E stained section of the mouse apex linguae. (b) Immunostaining with anti-podoplanin of the section adjacent to a. Lymphatic vessels expressing podoplanin in the tunica muscularis are visualized in green. The glandula lingualis is also immunostained with anti-podoplanin (arrow). (c) Merged image of immunostaining with anti-podoplanin and anti-PECAM-1. Lymphatic vessels expressing podoplanin and PECAM-1 are visualized in yellow green while blood vessels expressing only PECAM-1 are visualized in red. (d) High-magnification image of the region highlighted in a box in c. Lymphatic vessels expressing podoplanin are visualized in green. The glandula lingualis is also immunostained with anti-podoplanin (arrow). (e) High-magnification image of the region highlighted in a box in c. Lymphatic and blood vessels expressing PECAM-1 are visualized in red. The expression of PECAM-1 is not observed in the glandula lingualis. (f) Merged image of d and e. Lymphatic vessels expressing both podoplanin and PECAM-1 are visualized in yellow green (arrowheads) while blood vessels expressing only PECAM-1 are visualized in red. Bar=100 µm.