Fig. 5.
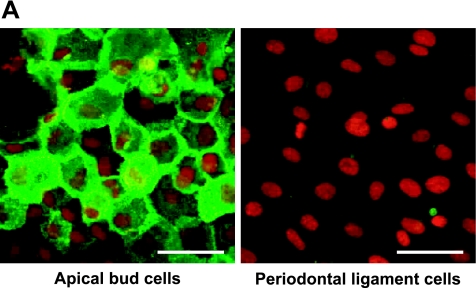
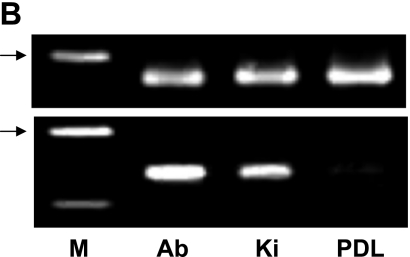
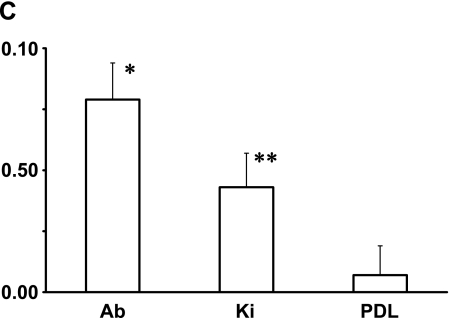
Analysis for the mouse apical bud. (A) Immunohistochemical analysis for cultured cells derived from the apical bud of lower incisor. Reaction products with anti-podoplanin are observed at cell-cell contacts of primary cultured cells surrounding the apical bud tissue whereas no immunoreactivity with anti-podoplanin is observed in cells derived from the periodontal ligament. Nuclei are stained by propidium iodide. Bar=100 µm. (B) RT-PCR analysis. Products of β-actin is shown in upper panel. Total RNA extracts from the tissue of apical bud (Ab) showed the PCR product for podoplanin mRNA (lower panel) as well as the tissue of kidney (Ki), whereas no products were detected in the tissue of periodontal ligament (PDL). M, molecular weight marker (489 bp, arrows). (C) Real-time PCR analysis. Relative adhesion molecule production units are expressed as arbitrary units. The amount of podoplanin mRNA in the total RNA extracts from the tissue of apical bud (Ab) is 2-fold compared with the amount in the total RNA extracts from kidney (Ki), whereas little was detected in the tissue of periodontal ligament (PDL). *, Significantly different from Ki and PDL. **, Significantly different from PDL.