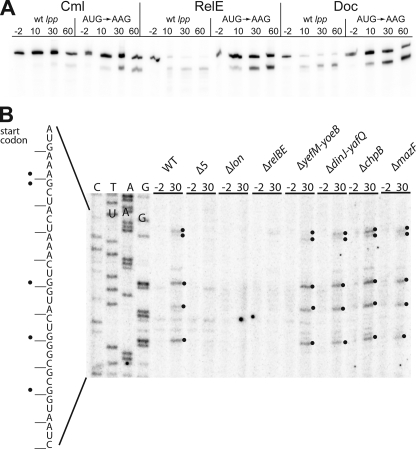
FIGURE 7.
Induction of RelE activity by Doc. A, Doc induces cleavage of a translated model lpp mRNA. Cells of MG1655Δlpp/MG3323 (pBAD-relE) and MG1655Δlpp/pMCD3303 (pBAD-doc) containing either of the plasmids pSC710 (wild-type (wt) lpp) or pSC711 (ATG start codon of lpp changed to AAG) were grown exponentially in LB medium at 37 °C. To induce transcription of the toxin genes, arabinose (0.2%) was added at time 0. As a control, the strains MG1655Δlpp/pSC710 and MG1655Δlpp/pSC711 were treated with chloramphenicol (Cml) (50 μg/ml) at time 0 to inhibit translation. Total RNA samples were fractionated by PAGE, and lpp mRNA was visualized by Northern blotting analysis. Numbers are time points of cell sampling relative to inhibition of translation by either chloramphenicol or arabinose. B, overproduction of Doc induces RelE-dependent mRNA cleavage. Primer extension analysis of lpp mRNA after transcriptional induction of doc from pMCD3303 (pBAD-doc) in the following strains: MG1655 (wild type), Δ5 (SC301467), Δlon, ΔrelBE (SC31), ΔyefM-yoeB (SC36), ΔdinJ-yafQ (SC37), ΔmazF (SC30), and ΔchpB (SC31). The strains were grown in LB medium to an A450 nm of 0.5, and total RNA was prepared from bacterial samples taken at the indicated time points (-2 and 30 min) after the addition of 0.2% arabinose. Primer extension was performed as described under “Experimental Procedures” using 32P-labeled primer lpp21. Significant cleavage sites in the RNA are marked with black dots on the gel and in the corresponding sequence to the left.