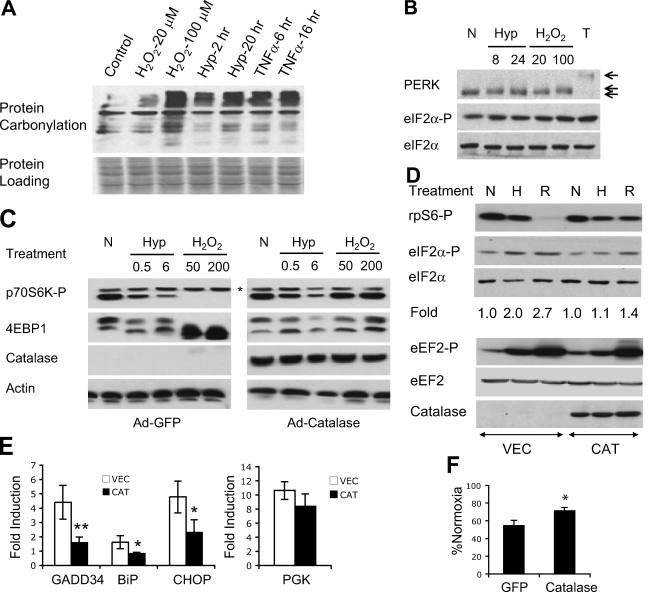
FIGURE 5.
Role of ROS during hypoxic regulation of mRNA translation. A, HEK293 cells were exposed to H2O (vehicle control), H2O2 (20 or 100 μm, 1 h), hypoxia (Hyp; 0.5% O2, 2 or 20 h), or TNFα (10 ng/ml, 6 or 16 h). Protein carbonylation in whole cell extracts was examined. Equivalent sample loading was based on Ponceau staining. B, HEK293 cells were exposed to hypoxia (0.5% O2, 8 or 24 h), H2O2 (20 or 100 μm, 1 h), or thapsigargin (T) (0.8 μm, 4 h). Mobility of total PERK proteins and phosphorylation of eIF2α were determined. C, MEFs infected with adenoviral GFP or catalase were exposed to hypoxia (0.5% O2, 0.5 or 6 h) or H2O2 (50 or 200 μm, 1 h). Phosphorylation of p70S6K and 4EBP1 was examined using anti-phospho-p70S6K (Thr389) and total 4EBP1 antibodies. *, the p80S6K isoform, which did not change appreciably during any treatments. The status of 4EBP1 is indicated by mobility shift from phosphorylated β form to hypophosphorylatedα form. D, HEK293 cells transfected with catalase or empty vector were exposed to 21% (N) or 0.5% O2 (H) for 20 h, or 50 μm H2O2 for 1 h (R). Phosphorylation of rpS6, eIF2α, and eEF2 proteins was determined. Quantitative changes in eIF2α phosphorylation are shown. E, expression of mRNA for GADD34, BiP, CHOP, and phosphoglycerate kinase in HEK293 cells transfected with catalase (CAT) or vector (VEC) following 20 h of 21% or 0.5% O2. F, protein synthesis in adenoviral GFP- or catalase-expressing MEFs after 48 h 0.5% O2.*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.