FIG. 2.
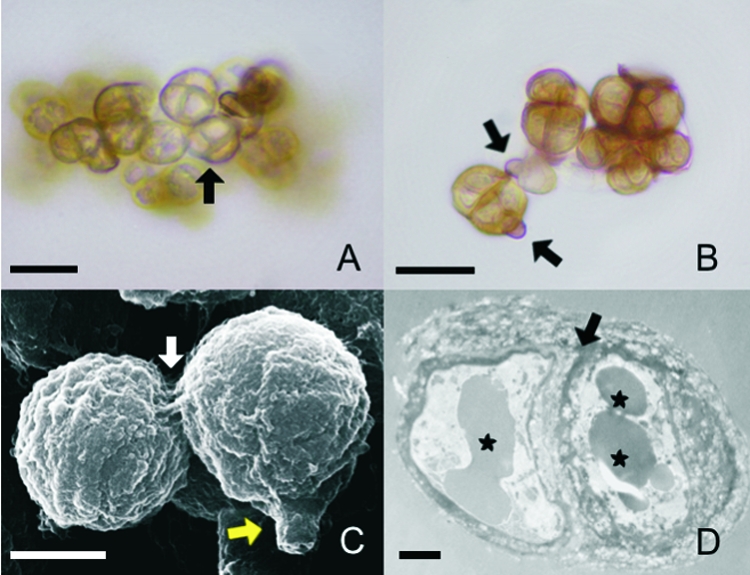
The morphological characteristics of sclerotic cells induced in either of the two natural media are similar. (A and B) Sclerotic cells obtained after culture of conidia in Theobroma grandiflorum or Bactris gasipaes natural media were analyzed by optical microscopy with no special staining. (A) Brownish, multiseptated cells (arrow) were evident. (B) Remnants of conidia adhering to the newly formed sclerotic cells (arrows) were observed. (C) SEM of aggregates of sclerotic cells demonstrates septated division (white arrow) and remnants of conidia (yellow arrow). (D) TEM of a sclerotic cell shows typical thick-walled septation (arrow) and vesicles containing electron-dense material (asterisks). Data are representative of one of three independent experiments, which were performed in triplicate. Bars, 10 μm (A and B), 5 μm (C), and 1 μm (D).
