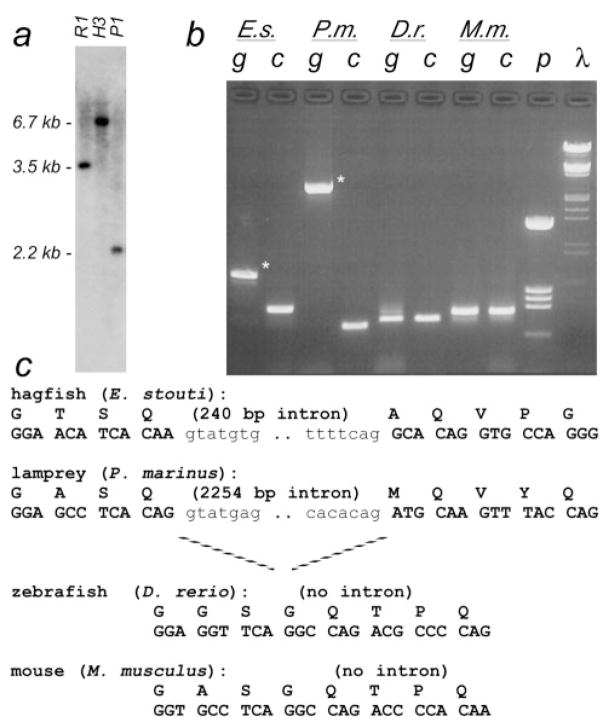
Fig. 3.
Intron/exon structure of TBP N-terminus. (a) Southern blot of hagfish genomic DNA using a probe to the Q/NC region. Sequence analysis of partial cDNA clones indicated the presence of Eco RI (R1), Hind III (H3), and Pst I (P1) sites in the 5′end of C-terminus–encoding sequences. The upstream portion of the 6.7-kb Hind III fragment (second lane) was cloned by ligation-mediated PCR, revealing an unexpected intron interrupting the NC region of the gene. (b) Distribution of intron C. Primers were designed to amplify across this novel splice junction from all vertebrates (E.s., hagfish; P.m., lamprey; D.r., zebrafish; M.m., mouse). Amplification of cDNA samples (lanes labeled “c”) confirmed that the primers worked in all species. Amplification of genomic DNA (“g”) showed a larger product in hagfish and lamprey (asterisks), indicating the region contained an intron in these species. λ, HindIII/EcoRI-cut λ-DNA markers; p, HinfI-cut pBS+ markers. (c) Genomic DNA and amino acid sequence of the junction region. Intron sequences in lowercase font.