Fig. 3.
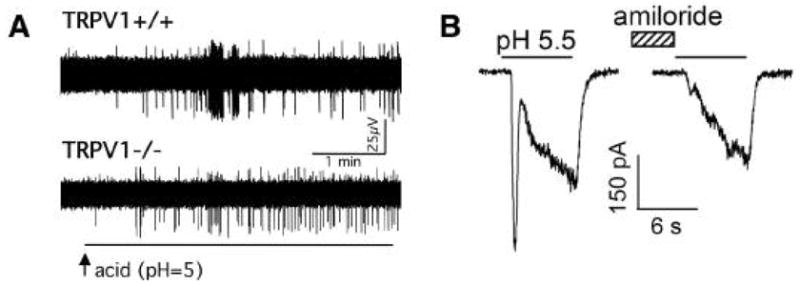
Acid-induced activation of the vagal bronchopulmonary C-fibres is mediated by the TRPV1 and TRPV1-independent receptors, likely the Acid Sensing Ion Channels. (A) Extracellular recordings from the bronchopulmonary C-fibres in the mouse lungs. The response to acid is attenuated (on average by ~50%) but not abolished in the TRPV1 knockout mouse. [From 58] (B) The whole-cell patch clamp recordings from the vagal sensory neurones in the rat. The lung-specific vagal neurones display transient amiloride-sensitive currents that are typical for the ASIC channels. [From 59]
