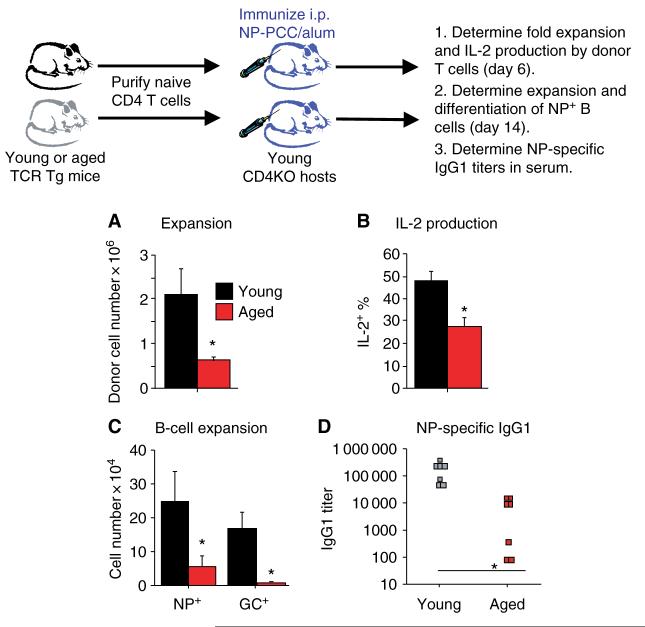
Fig. 3. Naive CD4+ T cells from aged mice exhibit reduced in vivo expansion and cognate helper function.
Purified populations of transgenic (Tg) CD4+ T cells from young (black) and aged (red) mice were transferred i.v. to CD4KO hosts (106 per host). Hosts were immunized with 200 μg of 4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl acetyl conjugated to PCC (NP-PCC)/alum i.p. on the same day. (A) On day 6, the recovery of donor T cells was determined by flow cytometry. Donor T cells were identified by CD4 Vβ3 staining. (B) On day 6, cells (spleen and lymph node) from the hosts were stimulated ex vivo with phorbol myristate acetate and ionomycin for 4 h and intracellular staining for interleukin (IL)-2 was performed. The percent of each donor CD4+ Vβ3 population staining positive for IL-2 was determined by flow cytometry. (C) On day 14, the number of NP-specific host B cells was determined by staining with NP conjugated to the fluorochrome allophycocyanin (NP-APC). The number of NP+ germinal center (GC) phenotype B cells (CD38lo PNAhi) was also determined by flow cytometry. (D) On day 14, serum was collected from each host and assayed for the presence of NP-specific immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) antibodies. For all graphs *P < 0.05 by Student’s t-test.