Figure 3.
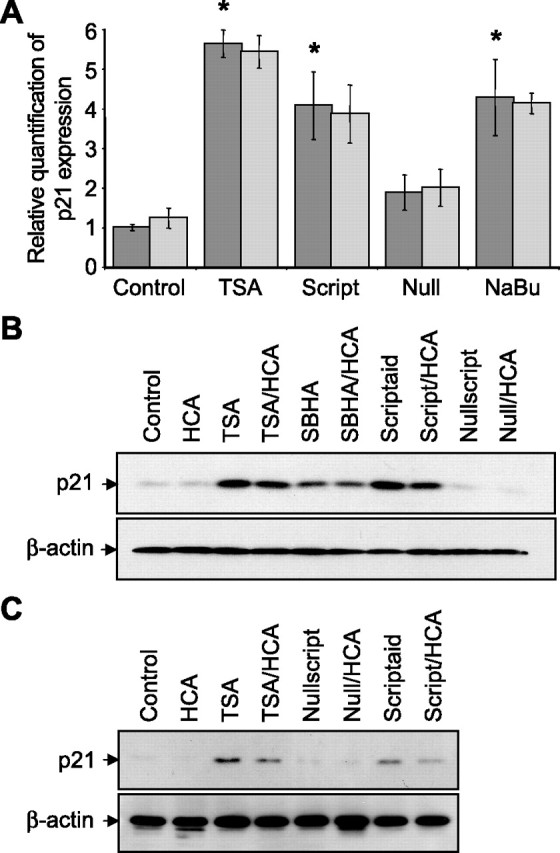
Structurally diverse HDAC inhibitors increase the expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, p21 in embryonic cortical neuronal cultures. A, Real-time PCR on cDNAs prepared from total RNA extracted from primary cortical neuronal cultures treated with TSA (0.66 μm), scriptaid (6.13 μm), nullscript (6.13 μm), and sodium butyrate (1 mm) treatments in the presence (light gray) or absence (dark gray) of HCA (5 mm) for 8 h. Control is no HDAC inhibitor. p21 amplification was normalized to β-actin in PCRs. Graph depicts mean fold increase in p21 expression relative to control ± SD. HCA has no significant effect on p21 expression by two-way ANOVA. *Significant difference from control, p < 0.01, by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple-comparisons test. B, Western blot analysis to detect relative levels of p21 in lysates from primary cortical neuronal cultures treated with TSA (0.66 μm), SBHA (12.5 μm), scriptaid (6.13 μm), and nullscript (6.13 μm). C, Western blot analysis to detect relative levels of p21 in lysates from primary cortical neuronal cultures after 2 h of incubation with HDAC inhibitor followed by 24 h of incubation with or without HCA (5 mm). HDAC inhibitors included TSA (1.32 μm), nullscript (12.3 μm), and scriptaid (12.3 μm). Relative levels of β-actin are shown to indicate loadings in Western blots. Antibodies against p21 or β-actin were used (see Materials and Methods).
