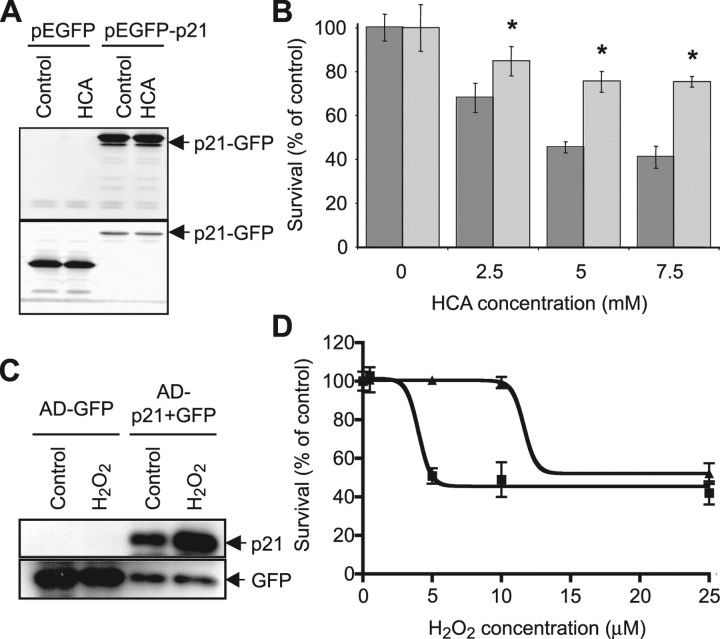
Figure 5.
p21 is sufficient for protection of neurons from oxidative stress-induced death. A, Western blot analysis to detect relative levels of GFP or p21-GFP fusion protein in lysates from HT22 murine hippocampal cells stably transfected with either pEGFP or pEGFP-p21 and treated with or without HCA (5 mm). Antibodies against p21 (top blot) or GFP (bottom blot) were used (see Materials and Methods). In addition to p21-GFP, the antibody for p21 detects endogenous p21, which is unchanged with HCA treatment. B, Graph showing viability of pEGFP- (dark gray) and pEGFP-p21- (light gray) transfected HT22 cells, as determined using the MTT assay, after treatment with increasing concentrations of HCA (2.5 mm to 7.5 mm) for 24 h. Graph bars depict mean ± SD. *Significant protection by p21 relative to GFP control, p < 0.001, by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni posttests. C, Western blot analysis to detect relative levels p21 or GFP in lysates from cortical neuronal cultures infected with either Ad-GFP or Ad-p21+GFP adenoviruses and treated with or without hydrogen peroxide (10 μm). Antibodies against p21 or GFP were used (see Materials and Methods). D, Graph showing viability of Ad-GFP- (squares) and Ad-p21+GFP- (triangles) infected cortical neuron cultures, as determined using the MTT assay, after treatment with increasing concentrations of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2; 1–25 μm) for 24 h. Goodness of fit for GFP: R2 = 0.968; and for p21: R2 = 0.963. EC50GFP = 4 μm [95% confidence interval (CI), 3.3–4.7 μm]. EC50p21 = 12 μm (95% CI, 9.1–14.1 μm). EC50GFP and EC50p21 are significantly different (p < 0.0001).