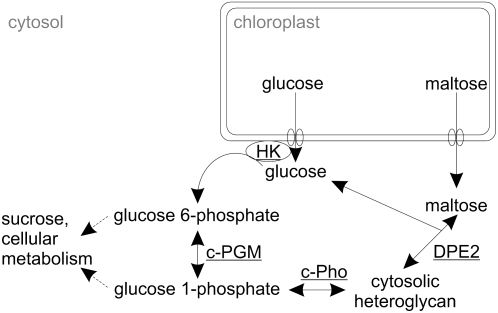
Figure 1.
Proposed cytosolic metabolism of starch-derived Glc and maltose following their export from the chloroplast. The carbon flux from the chloroplast to the cytosol is restricted to the export of two neutral sugars, maltose and Glc, via the Glc and maltose transporter. Both the cytosolic transglucosidase (DPE2) and the cytosolic phosphorylase isozyme (c-Pho) transfer glucosyl residues to the cytosolic heteroglycans. Both maltose and Glc-1-P act as glucosyl donors. Due to the reversibility of the two glucosyl transfer reactions, glucosyl residues can also be transferred from the nonreducing ends of the heteroglycans to Glc or to orthophosphate, yielding maltose and Glc-1-P, respectively. The cytosolic hexokinase (HK) is thought to be associated with the outer envelope membrane of the chloroplast.