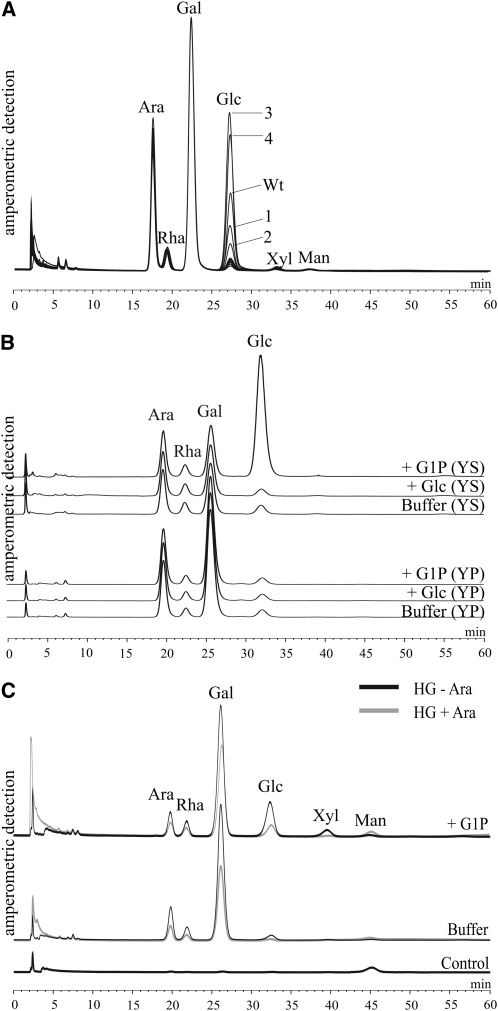
Figure 7.
Glc-1-P-related changes in SHGL. A, Discs were prepared from tubers of transgenic potato plants that possess elevated (lines 3 and 4) or decreased (lines 1 and 2) levels of the cytosolic phosphorylase isozyme. As a control, tubers from wild-type plants (Wt) were used. Following the incubation with Glc-1-P for 30 min, SHGL was isolated and hydrolyzed and the resulting monosaccharide pattern was analyzed by HPAEC-PAD. From each preparation, equal amounts of monosaccharides (4 μg of Glc equivalents each) were applied to the column. For each line, a typical chromatogram from three independently performed experiments is shown. B, Monosaccharide patterns of the Yariv-reactive (subfraction II; YP) or the Yariv-nonreactive (subfraction I; YS) subfractions of SHGL that had been isolated from tuber discs (wild type) following 60 min of incubation. As controls, tubers were incubated in a medium in which Glc-1-P was either omitted (buffer) or replaced by equimolar Glc. Equal amounts of carbohydrates (4 μg of Glc equivalents each) were applied to the HPAEC column. A typical chromatogram from two independently performed experiments is shown. C, SHGL (20 μg) prepared from tuber discs (wild type) following 20 min of incubation with Glc-1-P was treated for 3 h with endo-α-1,5-arabinanase from A. niger. Subsequently, compounds having an apparent size of less than 10 kD were removed by membrane filtration and the residual >10-kD material was subjected to acid hydrolysis and applied to the column. As a control, arabinanase was incubated in the absence of the SHGL preparation. A typical chromatogram from three independently performed experiments is shown.