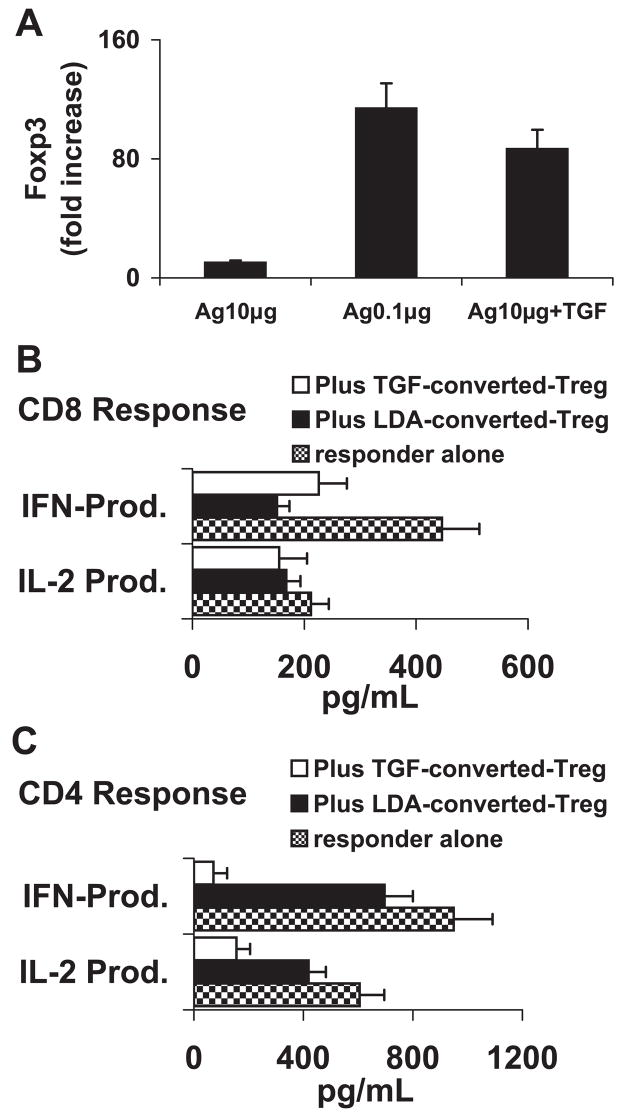
Figure 5.
CD8+CD122− T cells gained suppressor activity after stimulation with low-dose antigen or high-dose antigen in the presence of TGF-β1. (A) CD8+CD122− T cells were isolated from IRBP1-20-immunized B6 mice, and stimulated for 48 hours in 12-well plates with 10 or 0.1 μg/mL IRBP1-20 10 μg/mL of IRBP1-20 plus 1 ng/mL TGF-β1. After an in vitro stimulation by low-dose antigen or high-dose antigen plus TGF-β1, the CD8+CD122− T cells expressed increased levels of Foxp3 (P < 0.01). (B, C) Freshly prepared CD8+CD122− (B) or CD4+CD25− (C) responder cells were incubated for 48 hours in 12-well plates (4 × 106 cells/well) with immunizing peptide (10 μg/mL) and APCs, in the absence or presence of the indicated Foxp3high CD8+CD122− Treg cells at a regulatory T cell to responder T cell ratio of 1:4, then IL-2 and IFN-γ in the culture supernatants were measured by ELISA. The results are representative of more than five experiments. LDA-converted-Treg: CD8CD122− T cells converted by low-dose antigen; TGF-β-converted Treg: CD8CD122− T cells converted by TGFβ1 (P < 0.01).