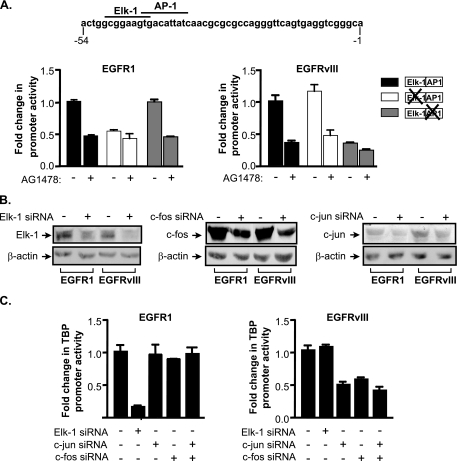
FIG. 4.
EGFR1 and EGFRvIII require different transcription factors to induce TBP promoter activity. (A) TBP promoter induction by EGFR1 requires an Elk-1 binding site, whereas EGFRvIII requires an AP-1 binding site. (Top) The human TBP promoter sequence denoting the Elk-1 and AP-1 sites located between −54 and −1 of transcriptional start site. U87 stable lines were transfected with the designated TBP promoter constructs together with a CMV-driven promoter β-galactosidase reporter construct. Luciferase activity was normalized to β-galactosidase activity, and changes were calculated based on untreated control. (B) Specific downregulation of Elk-1, c-fos, or c-jun expression in EGFR1- and EGFRvIII-expressing U87 cells. Cells were transfected with either mm control siRNA (−) or siRNAs specific for Elk-1, c-fos, or c-jun. Lysates were prepared, and immunoblot analysis was performed using antibodies against Elk-1, c-jun, c-fos, or β-actin. (C) EGFR1 requires Elk-1, whereas EGFRvIII requires c-fos and c-jun for TBP promoter induction. U87 stable cell lines were cotransfected with the TBP promoter and either mm (−), Elk-1, c-jun, or c-fos siRNAs (+). Resultant lysates were analyzed for luciferase activity. Luciferase activities were normalized to total protein levels, and cells transfected with mm siRNA were set to 1. Changes were calculated based on activities in cells transfected with mm siRNA.