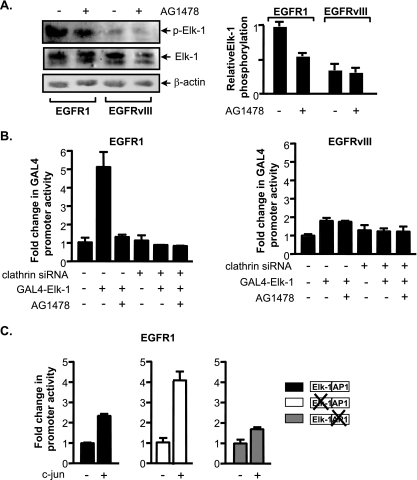
FIG. 6.
EGFR1 and EGFRvIII differentially affect Elk-1 function and c-jun expression. (A) EGFR1, but not EGFRvIII, enhances Elk-1 phosphorylation. (Left) Immunoblot analysis performed on lysates derived from U87 stable lines using antibodies specific for Elk-1 phospho-serine 383, Elk-1, and β-actin antibodies. (Right) For quantification of the relative levels of p-Elk-1, changes (n-fold) were calculated based on β-actin normalized protein levels in untreated U87-EGFR1 using three independent experiments. (B) Elk-1 transactivation function in EGFR1- and EGFRvIII-expressing cells. U87 stable cell lines were cotransfected with a Gal4-responsive promoter-luciferase construct containing a vector and either an Elk-1-Gal4 fusion protein expression vector or an empty vector. All cells were cotransfected with a CMV-driven β-galactosidase reporter construct. Resultant cell lysates were analyzed for luciferase and β-galactosidase activities. Change was calculated based on normalization to luciferase activity in untreated vector control cells transfected with mm siRNA. (C) Increased c-jun expression drives TBP promoter activity through the AP-1 site in EGFR1-expressing cells. Cells were cotransfected with wild-type or mutated TBP promoter constructs, a CMV-driven β-galactosidase reporter construct, and a c-jun expression vector. Resultant lysates were measured for luciferase and β-galactosidase activities. For all experiments, luciferase activities were normalized to β-galactosidase activity and the relative change was determined by setting the luciferase activity with empty vector to 1.