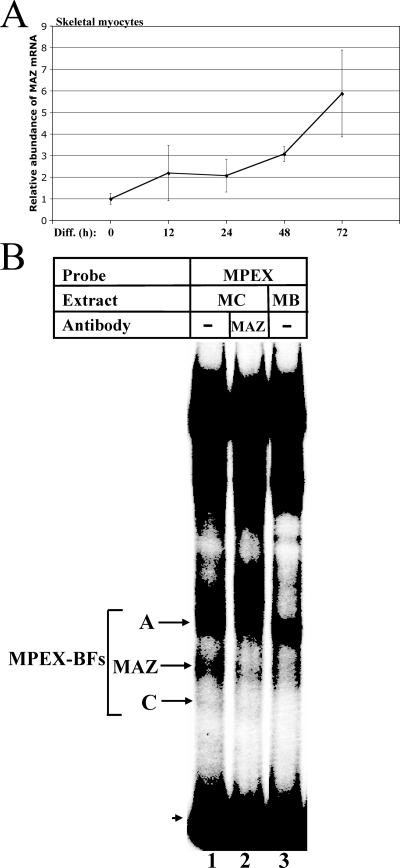
FIG. 6.
MAZ transcripts and DNA-binding activity are upregulated during skeletal myocyte differentiation. (A) MAZ transcripts increase during skeletal myocyte differentiation. MM14 skeletal myoblasts were allowed to differentiate for 0, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h and then harvested, and RNA was isolated. qRT-PCR was performed using primers specific to MAZ or 18S rRNA. Data are represented as the n-fold change in mRNA abundance for MAZ relative to 18S rRNA. Student's t test P values are 0.001 for 0 h versus 48 h and 0.05 for 0 h versus 72 h. (B) MAZ DNA-binding activity increases during skeletal myocyte differentiation. Labeled MPEX probe was mixed with 2 μg of either MM14 skeletal myocyte (MC) or myoblast (MB) nuclear extracts and analyzed via gel shift assay. The MAZ-specific band (reduced by MAZ-specific antibodies; lane 2) is indicated. The arrowhead indicates free probe.