FIG. 1. Angiotensin II activates p42/p44 MAP kinases independent of EGF-R transactivation; phosphospecific anti-caveolin-1 antibody cross-reacts with a 75 kDa protein.
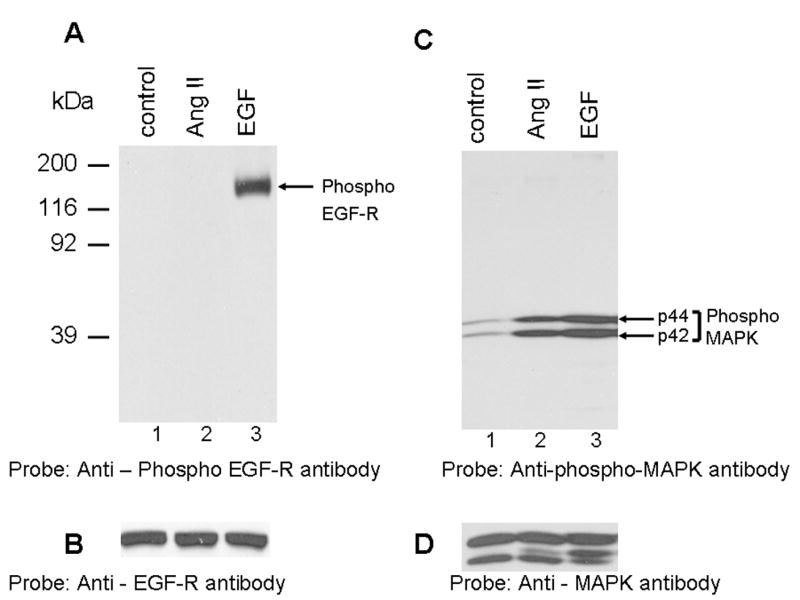
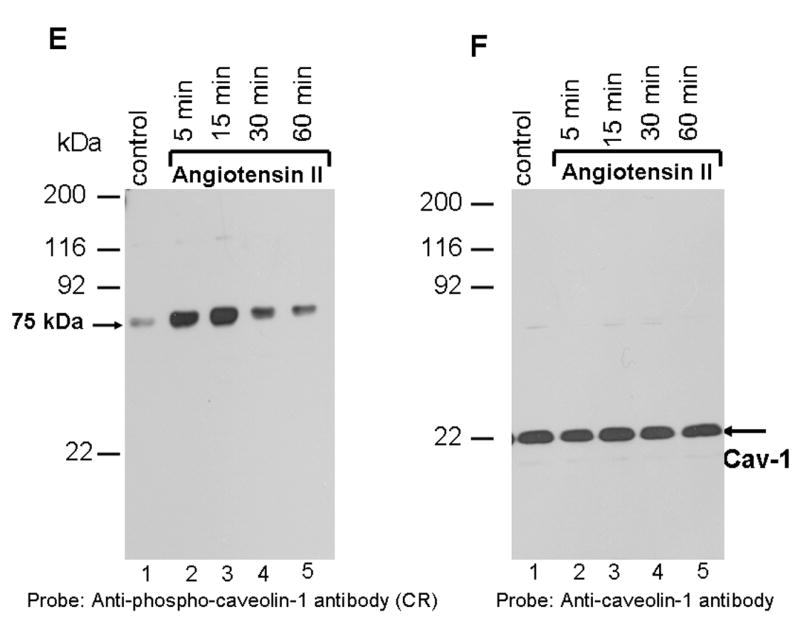
A, shows that Ang II does not transactivate EGF-R. Lysates were prepared from cells untreated (control), or treated with Ang II (100 nM, 3 min), or EGF (100 ng/ml; 3 min). Equal amount of proteins were run on a SDS-polyacrylamide gel and immunoblotted with phospho-specific EGF-R antibody specific for Y1068. B, the blot in A was stripped and reprobed with EGF-R antibody. C, shows that Ang II and EGF activate p42/p44 MAP kinases. The samples representing A were run on a SDS-polyacrylamide gel and immunoblotted with phospho-specific p42/p44 anti-MAP kinase antibody. D, The blot in C was stripped and reprbed with p42/p44 anti-MAP kinase antibody. E, shows that Ang II does not induce tyrosine phosphorylation of caveolin-1; anti-phospho caveolin-1 antibody cross reacts with a 75 kDa protein. Serum starved cells were left untreated (control) (lane 1), or treated with Ang II (100 nM) for different times (lanes 2–5), and total extracts were prepared, run on a 8% SDS-polyacrylamide gel, and immunoblotted with phospho-specific anti-caveolin-1 antibody. F, The blot in E was stripped and reprobed with anti-caveolin-1 antibody. These blots are representative of four independent experiments. The position of the 75 kDa protein and p42/p44 MAP kinases are shown in an arrows. CR, cross-reactive.
