FIG. 2. The 75 kDa protein detected by phospho-specific anti-caveolin-1 antibody is tyrosine and serine phosphorylated in Ang II-treated cells.
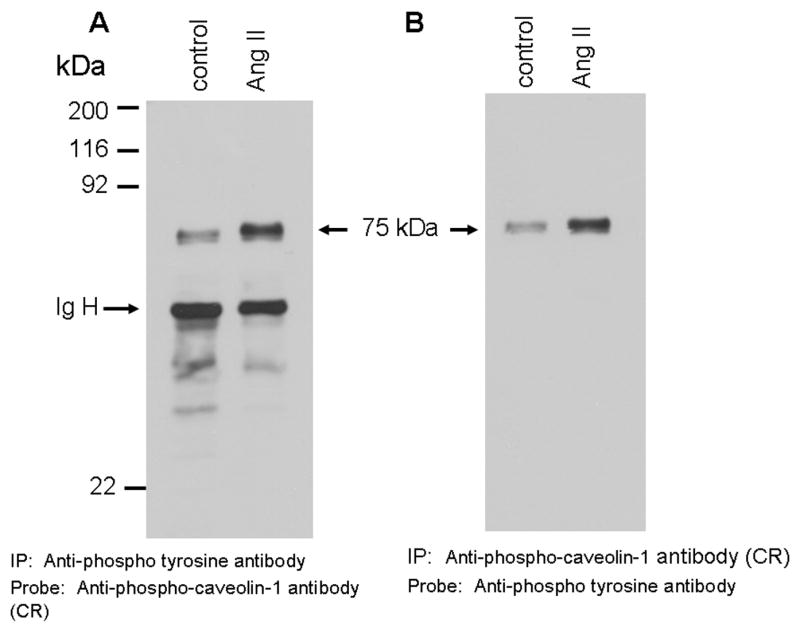
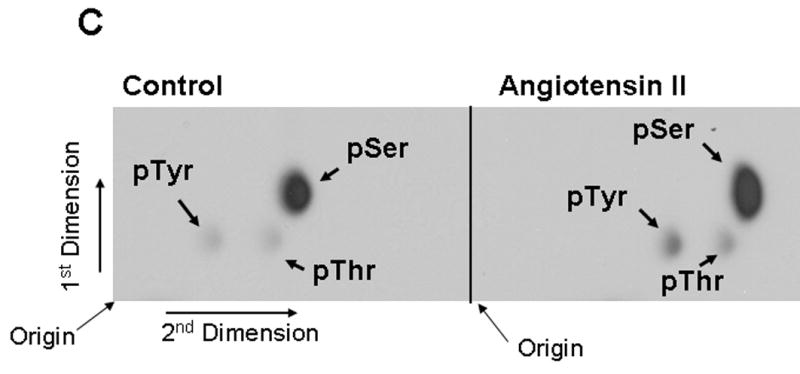
A and B show that Ang II-induces tyrosine phosphorylation of the 75 kDa protein. A, Serum starved cells were left untreated (control) or treated with Ang II (100 nM) for 15 min. Total cell lysates prepared and immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-phospho-tyrosine antibody, immunocomplexes were run on a 8% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and immunoblotted with phosphospecific anti-caveolin-1 antibody. B, Lasates representing A were immunoprecipitated (IP) with phosphospecific anti-caveolin-1 antibody, immunocomplexes were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-phospho-tyrosine antibody. C, Phosphoamino acid analysis of the 75 kDa protein following Angiotensin II treatment. Following in vivo labeling with [32P] as described in methods, cells were exposed to Ang II (100 nM) for 15 min. Five hundred μg of the total protein were immunoprecipitated with phospho-specific anti-caveolin-1 antibody (cross-reactive to the 75 kDa protein), run on a SDS-polyacrylamide gel, transferred to PVDF membrane, and exposed to X-ray film. The 75 kDa band from control and Ang II treated lanes were excised and subjected to phosphoamino acid analysis as described in the methods section. These blots are representative of four independent experiments. These blots are representative of four independent experiments. Ig H, Immunoglobulin heavy chain. CR, cross-reactive.
