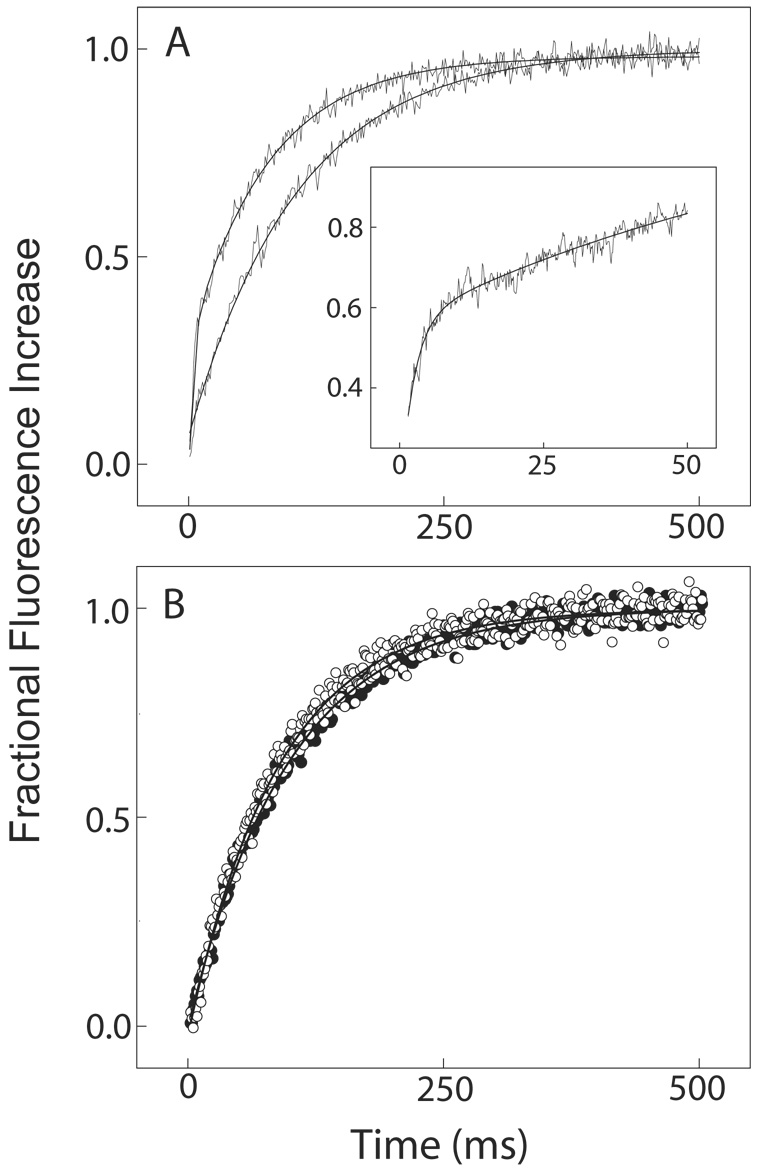
Fig. 3. Dissociation of Ca2+ from the complex between BSCaMIQ and CaM or NxCCaM.
The fluorescent Ca2+ chelator quin-2 was used as a Ca2+ trap. Dissociation of Ca2+ from native or mutant CaM therefore corresponds directly with a Ca2+-dependent increase in quin-2 fluorescence. A range of quin-2 concentrations was investigated to ensure that a concentration sufficient to prevent rebinding of Ca2+ was used. (A) Dissociation of Ca2+ from free CaM (lower trace) and from the CaM-BSCaMIQ complex (upper trace). The quin-2 fluorescence time course for Ca2+ dissociation from free CaM was generated by mixing a solution containing 4 µM CaM and 50 µM CaCl2 with an equal volume of 400 µM quin-2. These data are fit by a single exponential with a rate constant of 10.3±0.7 s−1 and an amplitude corresponding with dissociation of ~2 Ca2+ ions. Dissociation of two additional Ca2+ ions occurred within the instrument dead time. The quin-2 fluorescence time course for Ca2+ dissociation from the CaM-BSCaMIQ complex was generated by mixing a solution containing 25 µM BSCaMIQ, 4 µM CaM and 50 µM CaCl2 with an equal volume of 400 µM quin-2. The data presented are fit by a double exponential. The slower process has an apparent rate constant of 14.7±0.5 s−1 and an amplitude corresponding with dissociation of ~2 Ca2+ ions. The faster rate was derived from data measured over a shorter time interval (inset). These data are fit by a double exponential with rate constants of 427.4±35 and 11.7±0.5 s−1, and respective amplitudes corresponding with dissociation of ~1.5 and ~2 Ca2+ ions. If the faster process is forced to have an amplitude corresponding with dissociation of 2 Ca2+ ions, then apparent rate constants of 473.4±37.9 s−1 and 12.9±0.7 s−1 are derived for the faster and slower rates. (B) Dissociation of Ca2+ from the NxCCaM-BSCaMIQ complex (●) and from free NxCCaM (○). For these experiments a solution containing 4 µM NxCCaM and 50 µM CaCl2 in the presence or absence of 25 µM BSCaMIQ was mixed with an equal volume of 400 µM quin-2. The two resulting quin-2 fluorescence time courses are essentially superimposable. Ca2+-dissociation rate constants of 10.8±0.6 s−1 and 11.8±0.5 s−1 were derived for free and bound NxCCaM from fits of these data to single exponentials with amplitudes corresponding to dissociation of ~2 Ca2+ ions.