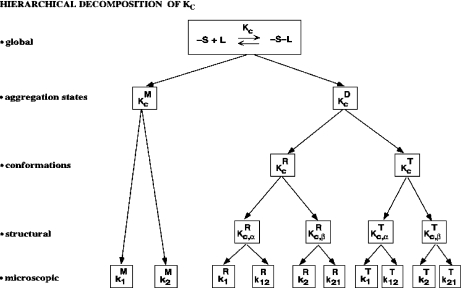
Fig. 7.
Hierarchical decomposition of the global association quotient, Kc, into partial association quotients, Kc,i, corresponding with the different hierarchical levels of binding, of the model system described in Fig. 6 and associated to the different subsystems: a aggregation level—the global system (S) is decomposed into two subsystems, monomer (M) and dimer (D); b conformational level—the dimer subsystem (D) is decomposed into two conformational subsystems, R and T; c structural level—the monomer (M) is divided into two structural subsystems corresponding to different primary structures of the subunits (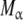 and
and 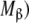 , and each conformation of the dimer is decomposed into two structural subsystems (R
, and each conformation of the dimer is decomposed into two structural subsystems (R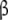 for conformation T); d microscopic level—the structural subsystems are decomposed into ten microscopic subsystems
for conformation T); d microscopic level—the structural subsystems are decomposed into ten microscopic subsystems