Abstract
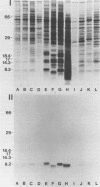
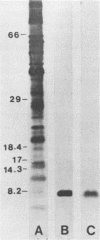
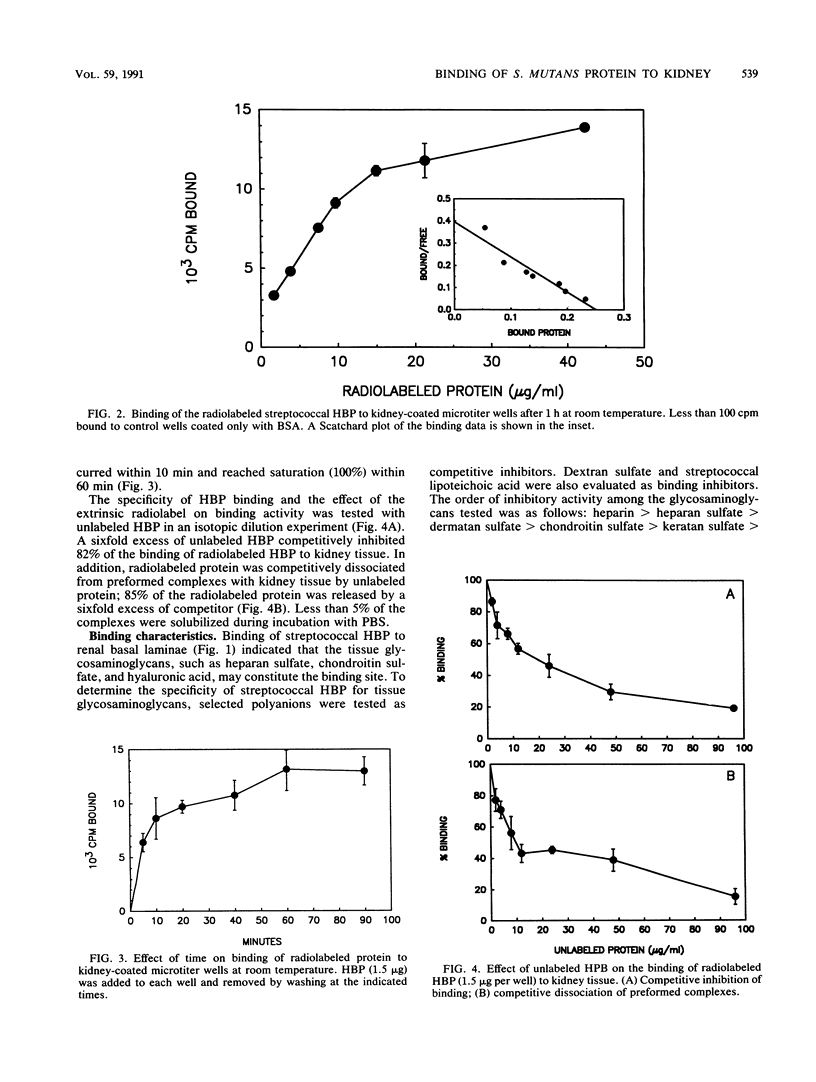
An 8-kDa protein, with binding activity for heparin and heparan sulfate of basal laminae of animal tissues, was isolated from Streptococcus mutans MT703 and purified to homogeneity. Binding of radioiodinated 8-kDa protein to rabbit kidney tissue in vitro showed a high degree of specificity, as indicated by saturation kinetics, time dependence, and competitive inhibition by unlabeled protein. Binding activity for kidney tissue was competitively inhibited by selected glycosaminoglycans and polyanions in the following order: heparin greater than dextran sulfate greater than heparan sulfate greater than chondroitin sulfate greater than lipoteichoic acid greater than keratan sulfate greater than hyaluronic acid. Binding of the streptococcal protein to rabbit kidney tissue was also strongly inhibited by protamine sulfate, polylysine, and a random copolymer of lysine and alanine. Among the monosaccharides tested at 50 mM, glucosamine 2,3- or 2,6-disulfate, glucuronic acid, glucose 6-phosphate, and glucose 6-sulfate inhibited 50% or more of the binding activity, whereas N-acetylglucosamine 3-sulfate, glucosamine 6-sulfate, N-acetyl-glucosamine, N-acetylgalactosamine, N-acetylneuraminic acid, and a selection of neutral sugars were not inhibitory. The heparin-binding protein was detected on the cell wall of S. mutans and in the culture medium following growth. Several other species of streptococci produce an immunologically related protein of similar size.
Full text
PDF

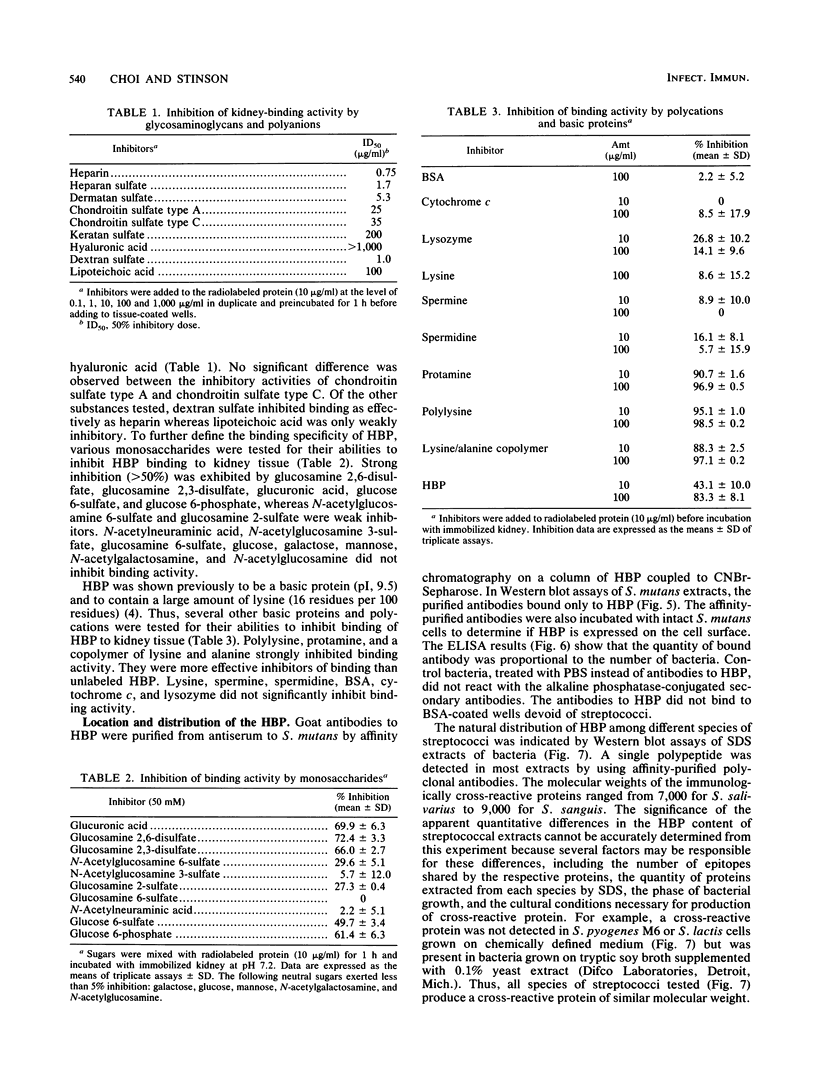
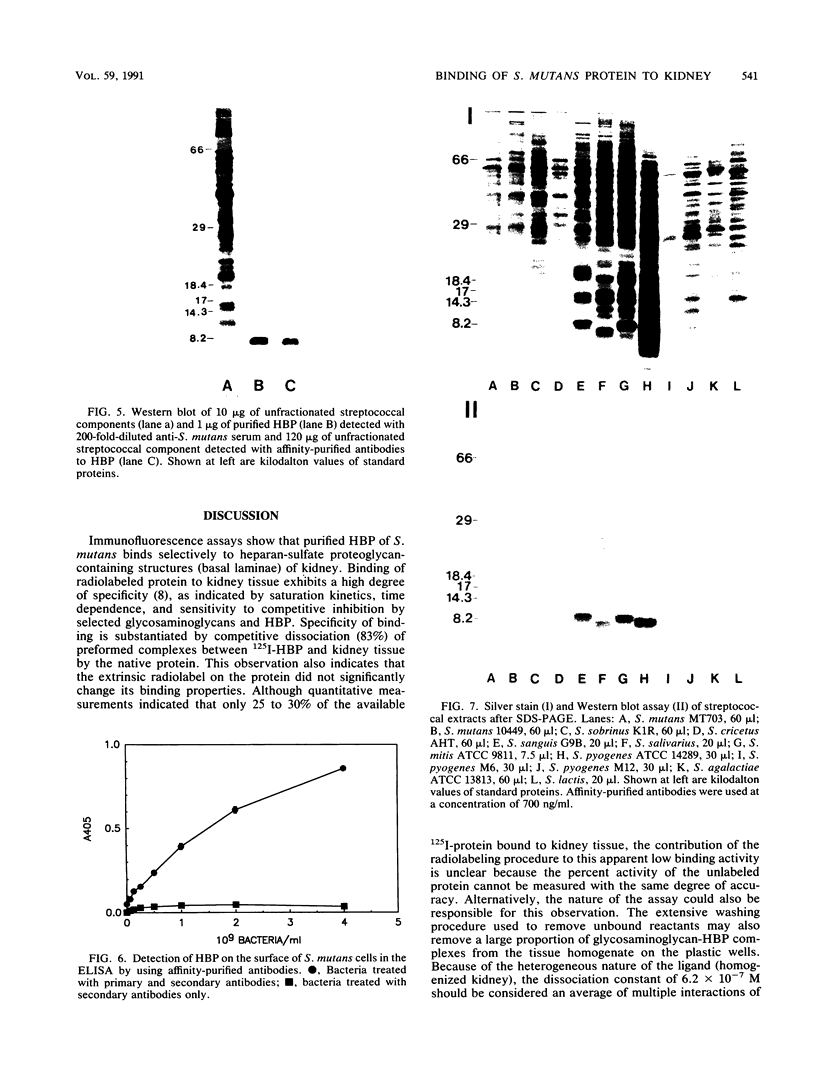


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albini B., Nisengard R. J., Glurich I., Neiders M. E., Stinson M. W. Streptococcus mutans-induced nephritis in rabbits. Am J Pathol. 1985 Mar;118(3):408–418. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez J., Alvarez L., Escudero C., Gilsanz F., de Oya S., Castillo-Olivares J. L. Hemodynamic and morphologic alterations after experimental administration of protamine sulfate. Am J Surg. 1988 Jun;155(6):735–740. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(88)80032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergey E. J., Stinson M. W. Heparin-inhibitable basement membrane-binding protein of Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1715–1721. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1715-1721.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi S. H., Stinson M. W. Purification of a Streptococcus mutans protein that binds to heart tissue and glycosaminoglycans. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3834–3840. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3834-3840.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. T., Lyon M., Steward W. P. Structure and function of heparan sulphate proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 1;236(2):313–325. doi: 10.1042/bj2360313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. Dental caries. Annu Rev Med. 1975;26:121–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.26.020175.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder E. J., Wilkowske C. J., Washington J. A., 2nd, Geraci J. E. Streptococcus mutans endocarditis. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Mar;80(3):364–368. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-3-364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Linker A., Farquhar M. G. Increased permeability of the glomerular basement membrane to ferritin after removal of glycosaminoglycans (heparan sulfate) by enzyme digestion. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):688–693. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leon O., Panos C. Cytotoxicity and inhibition of normal collagen synthesis in mouse fibroblasts by lipoteichoic acid from Streptococcus pyogenes type 12. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):785–794. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.785-794.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W. L. Leakage of blood-retinal barrier due to damaging effect of protamine sulfate on the endothelium. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;76(4):427–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00686981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood W. R., Lawson L. A., Smith D. L., McNeil K. M., Morrison F. S. Streptococcus mutans endocarditis. Report of a case. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Mar;80(3):369–370. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-3-369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):353–380. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.353-380.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. R., Michalek S. M. Immunobiology of dental caries: microbial aspects and local immunity. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:595–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. B., Krieger A. G., Schiller N. L., Gross K. C. Viridans streptococcal endocarditis: the role of various species, including pyridoxal-dependent streptococci. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Nov-Dec;1(6):955–966. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.6.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler M. W., Venkatachalam M. A., Cotran R. S. Glomerular epithelium: structural alterations induced by polycations. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):390–393. doi: 10.1126/science.1145209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Barua P. K., Bergey E. J., Nisengard R. J., Neiders M. E., Albini B. Binding of Streptococcus mutans antigens to heart and kidney basement membranes. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):145–151. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.145-151.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Nisengard R. J., Neiders M. E., Albini B. Serology and tissue lesions in rabbits immunized with Streptococcus mutans. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):3021–3027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartzwelder F. J., Barua P. K., Albini B., Stinson M. W. Heart-reactive antibodies in rabbit anti-Streptococcus mutans sera fail to cross-react with Streptococcus mutans. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):954–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleckyj B., Willett N. P., Shockman G. D. Growth of several cariogenic strains of oral streptococci in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.649-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson K., Leon O., Panos C. Morphological changes and pathology of mouse glomeruli infected with a streptococcal L-form or exposed to lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1144–1151. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1144-1151.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt A., Batsford S., Rodríguez-Iturbe B., García R. Cationic antigens in poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol. 1983 Dec;20(6):271–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]