Abstract
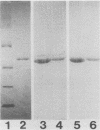
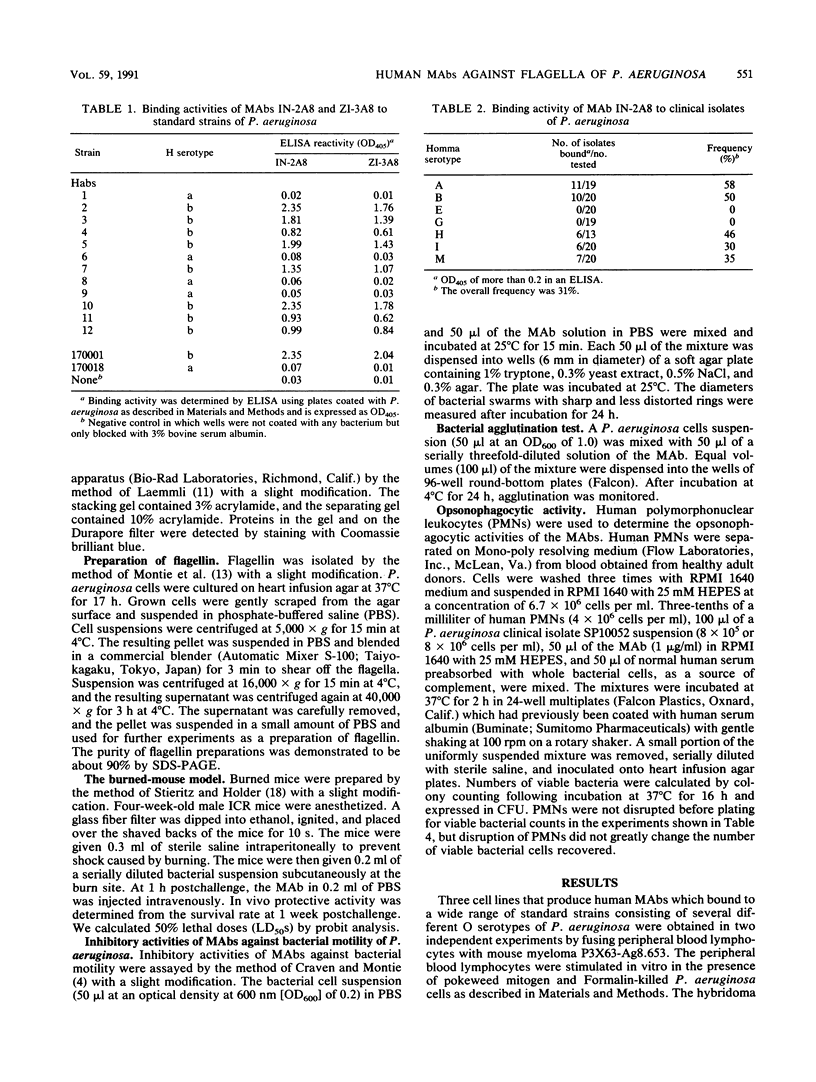
Three stable hybridoma cell lines, IN-2A8, IN-5D6, and ZI-3A8, that secrete human monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) specific for b-type flagella of Pseudomonas aeruginosa were established by fusing peripheral blood lymphocytes from healthy volunteers with murine myeloma P3X63-Ag8.653 cells. The immunoglobulin M MAbs reacted specifically with flagellin (Mr, 52,000) by Western blotting (immunoblotting) analysis and bound specifically to clinical isolates belonging to Homma serotypes A, B, H, I, and M at frequencies of 58, 50, 46, 30, and 35%, respectively, but did not bind to any serotype E or G isolates. Overall, the MAbs bound to 31% of the clinical isolates. MAb IN-2A8 strongly protected burned mice challenged with P. aeruginosa bearing b-type flagella from death following parenteral administration of 0.1 microgram per mouse. This MAb also inhibited P. aeruginosa colony spreading in soft agar at a concentration of more than 1 microgram/ml but only slightly enhanced opsonophagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. A line of evidence suggests that the potent in vivo activity of MAb IN-2A8 in the burned-mouse model is likely to be caused by its inhibition of bacterial motility after binding to flagella.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson T. R., Montie T. C. Flagellar antibody stimulated opsonophagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with response to either a- or b-type flagellar antigen. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Sep;35(9):890–894. doi: 10.1139/m89-148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson T. R., Montie T. C. Opsonophagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa treated with antiflagellar serum. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3204–3206. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3204-3206.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansorg R. A., Knoche M. E., Spies A. F., Kraus C. J. Differentiation of the major flagellar antigens of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by the slide coagglutination technique. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):84–88. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.84-88.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven R. C., Montie T. C. Motility and chemotaxis of three strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa used for virulence studies. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Apr;27(4):458–460. doi: 10.1139/m81-070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Pitt T. L., Fürer E., Germanier R. Role of lipopolysaccharide in virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):508–513. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.508-513.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doig P., Smith N. R., Todd T., Irvin R. T. Characterization of the binding of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alginate to human epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1517–1522. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1517-1522.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake D., Montie T. C. Protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection by passive transfer of anti-flagellar serum. Can J Microbiol. 1987 Sep;33(9):755–763. doi: 10.1139/m87-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Mutharia L. M., Chan L., Darveau R. P., Speert D. P., Pier G. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis: a class of serum-sensitive, nontypable strains deficient in lipopolysaccharide O side chains. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):170–177. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.170-177.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder I. A., Wheeler R., Montie T. C. Flagellar preparations from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: animal protection studies. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):276–280. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.276-280.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma J. Y. Designation of the thirteen O-group antigens of Pseudomonas aeruginosa; an amendment for the tentative proposal in 1976. Jpn J Exp Med. 1982 Dec;52(6):317–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lányi B. Serological properties of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. II. Type-specific thermolabile (flagellar) antigens. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1970;17(1):35–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montie T. C., Craven R. C., Holder I. A. Flagellar preparations from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):281–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.281-288.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montie T. C., Doyle-Huntzinger D., Craven R. C., Holder I. A. Loss of virulence associated with absence of flagellum in an isogenic mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the burned-mouse model. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1296–1298. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1296-1298.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Iglewski B. H. The contribution of exoproducts to virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Apr;31(4):387–392. doi: 10.1139/m85-074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninnemann J. L. Clinical and immune status of burn patients. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1987;39:16–25. doi: 10.1159/000414330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M. The role of exotoxin A in pseudomonas disease and immunity. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;5 (Suppl 5):S979–S984. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_5.s979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieritz D. D., Holder I. A. Experimental studies of the pathogenesis of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: description of a burned mouse model. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jun;131(6):688–691. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.6.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Berry V. K., Bass J. A. Role of pili in adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to mammalian buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1146–1151. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1146-1151.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretlind B., Pavlovskis O. R. Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase and its role in pseudomonas infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;5 (Suppl 5):S998–1004. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_5.s998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota S., Ochi H., Ohtsuka H., Kato M., Noguchi H. Heterogeneity of the L-rhamnose residue in the outer core of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide, characterized by using human monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1691–1696. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1691-1696.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]