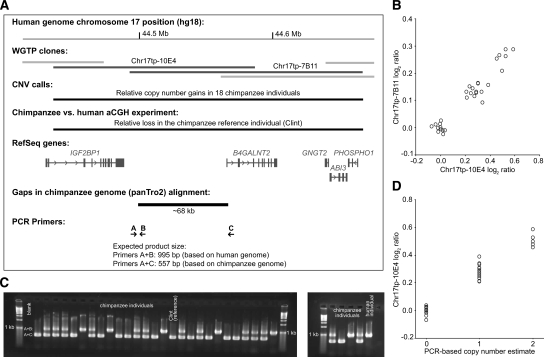
Figure 2.
PCR-based validation of a deletion CNV in chimpanzee. (A) The WGTP clones Chr17tp-10E4 and Chr17tp-7B11 (human chromosome 17q21.32) report a chimpanzee-specific deletion CNV. Based on an alignment of the chimpanzee and human genomes (Karolchik et al. 2003) for this region, the chimpanzee reference sequence (donor: Clint) has a gap of ∼68 kb including the first exon of the B4GALNT2 gene. In the between-species aCGH experiment, we observed a relative loss for these two clones in Clint compared with the human reference individual. (B) Bivariate clustering of Chr17tp-10E4 and Chr17tp-7B11 log2 ratios. The inferred cluster class of Clint, the chimpanzee reference individual (i.e., log2 ratio close to 0 for each clone) corresponds to the lowest copy number state among chimpanzees. (C) Results of a PCR-based genotyping assay using a 1.2% agarose gel with ethidium bromide staining. PCR primer positions are depicted in A. Note that primer combination A+C amplifies only when the intervening sequence is deleted. The 31 chimpanzees (including Clint) are in sample numerical order. One human individual is included as positive control. (D) PCR-based copy number genotype estimates and Chr17tp-10E4 log2 ratio clusters are 100% concordant.