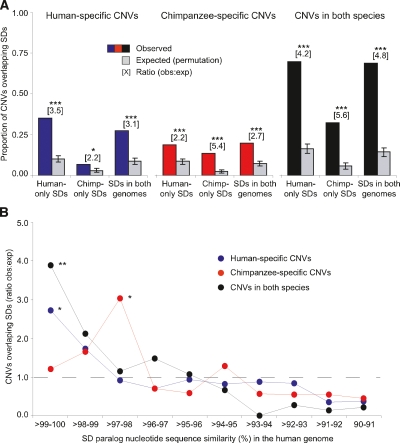
Figure 5.
Colocalization of CNVs and SDs in the human and chimpanzee genomes. (A) Observed and expected proportion of human-specific CNVs (i.e., human CNVs that do not overlap any chimpanzee CNVs), chimpanzee-specific CNVs, and CNVs that were observed in orthologous regions in both species that overlap human-only, chimpanzee-only, and shared SDs. A given CNV may intersect more than one type of SD. Expected values are based on 10,000 randomized permutations. (B) Ratio of observed (obs) versus expected (exp) number of common CNVs (observed in two or more individuals) overlapping SDs in the human genome, binned by nucleotide sequence similarity between intrachromosomal SD paralogs. For CNVs overlapping multiple SDs, the SD with maximum (similarity x length) is reported. Expected values are based on 1000 randomized permutations. *P < 0.01; **P < 0.001; ***P < 1 × 10−8.