Figure 5. Chemotaxis is inhibited by overexpression of constitutively active CKLiK.
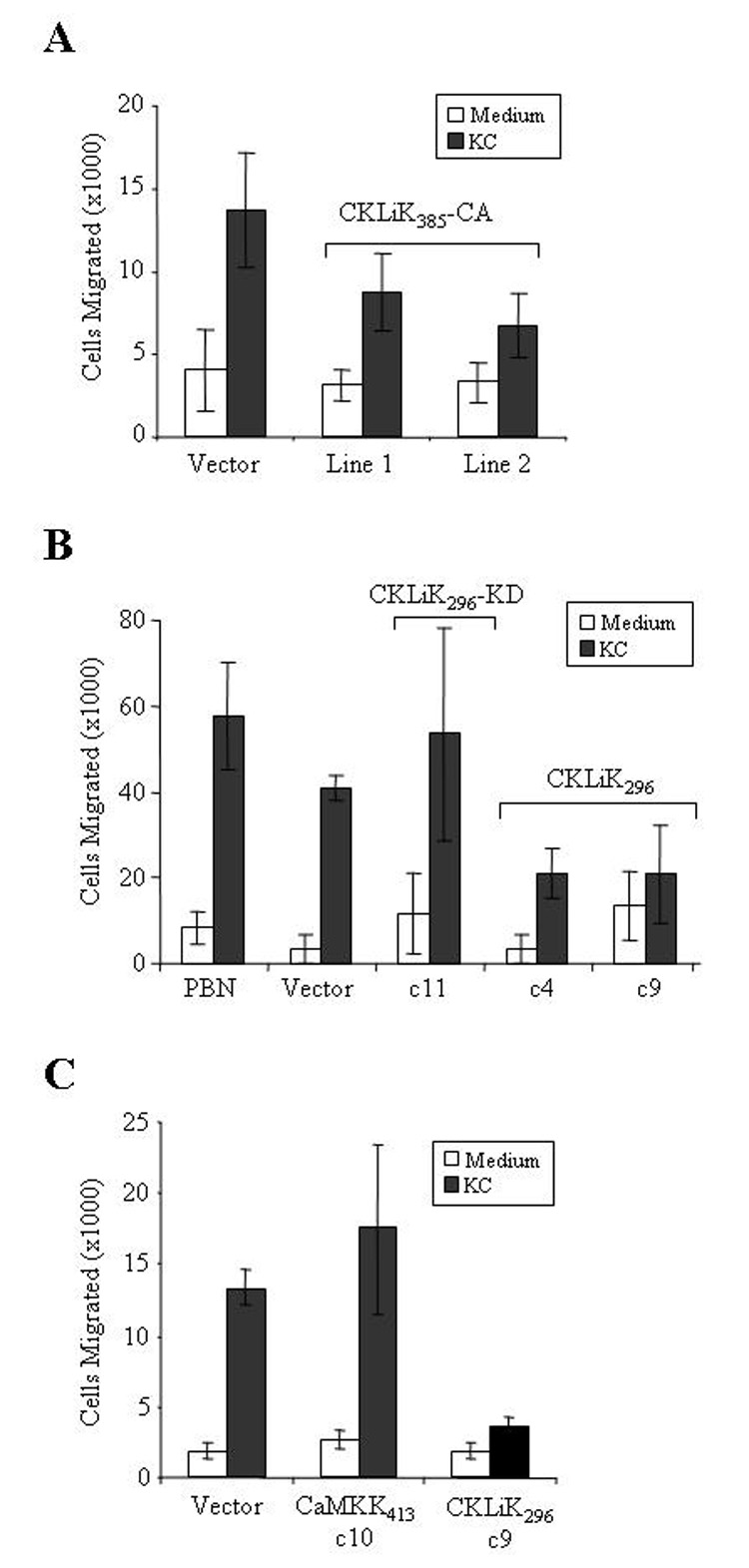
(A) Expression of the full-length, constitutively active CKLiK inhibits chemotaxis. Chemotaxis assays were performed using ATRA induced cells and transwell plates with 3 µm membranes. Graphed are the average total number of cells ± SD that migrated after a 2 hour incubation into the bottom chamber containing medium only or KC. P values generated by the Student’s two sample t-test (Excel, Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA) for the differences between chemotaxis by cells expressing the vector versus CKLiK385-CA are as follows: vector vs. line #1, p = 0.004; vector vs. line #2, p = 0.0006. Data shown are from triplicate experiments performed in parallel. (B) EPRO cells that express CKLiK296 exhibit reduced chemotaxis as compared to cells expressing the empty vector or CKLiK296-KD, or to peripheral blood neutrophils (PBN). Statistical analyses yielded the following results: vector vs. CKLiK296-KD c11, p = 0.15 (not statistically different); vector vs. CKLiK296 c4, p = 0.005; vector vs. CKLiK296 c9, p = 0.009. (C) Ectopic expression of CaMKK413 does not disrupt chemotaxis, as demonstrated by levels of cell migration similar to that observed by cell expressing the empty vector. P values: vector vs. CaMKK413 c10, p = 0.23 (not statistically different), vector vs. CKLiK296 c9, p = 0.00008.
