Figure 2.
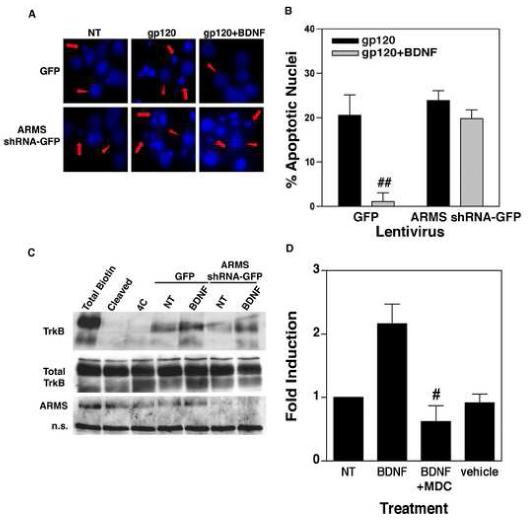
(A) Neuroprotective effect of BDNF is mediated by ARMS. Primary cortical neurons infected with ARMS shRNA-GFP or GFP lentivirus were treated with BDNF (100 ng/ml) for 18 hours, followed by incubation of the cells with gp120 (5nM) for an additional 72h. Staining of the cultures with Hoechst 33342 dye revealed a higher percentage of apoptotic nuclei in gp120-exposed cells (middle panels). Whereas, co-administration of BDNF inhibited gp120-induced apoptosis in control cells (cells expressing GFP alone, upper right panel) but not in ARMS shRNA-GFP expressing cells (lower right panel). Apoptotic cells are marked with arrows, whereas arrow-heads show healthy cells. (B) Quantitative analysis of data from three independent experiments that examined survival of neurons as outlined above. The data are presented as Mean ± SEM of percent apoptotic neurons. ## indicates P<0.01 as compared to gp120-treated control cells (GFP, filled bar). (C) Loss of ARMS does not affect BDNF-induced internalization of TrkB. Surface proteins of cells infected with ARMS shRNA-GFP or GFP expressing lentivirus were labeled by EZ Link Sulfo NHS-SS-biotin. TrkB internalization was then initiated by incubation with BDNF (100 ng/ml) for 30 minutes at 37°C. Glutathione cleavage buffer removed the remaining biotin on the cell surface. The biotinylated, internalized TrkB was precipitated by streptavidin followed by immunoblot using a TrkB antibody. Both full-length (145 kD) and truncated (95 kD) TrkB receptors are shown. Total surface biotinylated TrkB (Total biotin) was measured in cells held on ice; the efficiency of biotin cleavage is demonstrated in (Cleaved); and spontaneous TrkB internalization induced by BDNF is shown (4C). Cells expressing either GFP lentivirus or ARMS shRNA-GFP expressing lentivirus exhibit similar levels of basal and BDNF-induced TrkB internalization. (D) Receptor internalization is required for BDNF-induced NF-κB transcriptional activity. DIV7 primary cortical neurons were transfected with NF-κB luciferase plasmid for 40 hours. Cells were then stimulated with BDNF (100ng/mL) alone, BDNF plus the internalization inhibitor, MDC (25μM), or vehicle alone for 8 hours. ‘NT’ represents non-treated cells. Analysis of luciferase gene expression (presented as a fold induction) shows that inhibition of receptor internalization blocks NF-κB activity induced by BDNF. The bars represents SEMs and the data is representative of three separate experiments. # indicates statistical significance p<0.05 as compared to BDNF-treated cells.
