Figure 4.
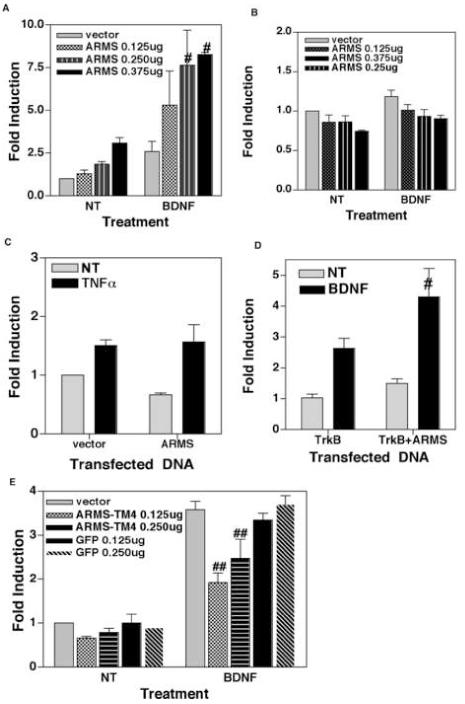
(A) Overexpression of ARMS augments BDNF-induced activation of NF-κB. DIV 7 cortical neurons were co-transfected with NF-κB luciferase reporter plasmid and either empty vector or increasing amounts of full-length ARMS plasmid. The recipient cells were then treated with BDNF (100ng/mL) for 8 hours and luciferase activity was measured. Data is presented as the mean (fold induction) of 3 independent observations, the bars represents SEM. # denotes p<0.05 as compared to untreated cells (NT). (B) Similar luciferase assays were performed to measure Oct-1 activity in cortical neurons. The results (Mean of fold induction ± SEM of 3 experiments) show that the over-expression of ARMS has no effect on Oct-1 activity. (C) Overexpression of ARMS does not influence TNFα mediated activation of NF-κB. NF-κB-dependent luciferase assays were performed in which HEK293 cells were treated with TNFα (20ng/mL) for 8 hours. Results revealed similar levels of NF-κB activity in untreated as well as TNFα-treated cells. (D) Expression of TrkB and ARMS is sufficient for BDNF to induce NF-κB activity. HEK293 cells were co-transfected with NF-κB luciferase reporter plasmid and TrkB alone, or TrkB plus full-length ARMS. After this, the recipient cells were treated as indicated. # denotes p<0.05 derived from three sets of experiments, shown as Mean of fold induction ± SEM. (E) Interaction between TrkB and ARMS is required for BDNF to induce NF-κB. Neuronal cells were co-transfected with an NF-κB luciferase reporter and indicated plasmids. ARMS-TM4 encodes transmembrane region (amino acids 2041 to 2673) of ARMS. Luciferase activity is presented as a mean of fold induction ± SEM. ## equals p<0.01.
