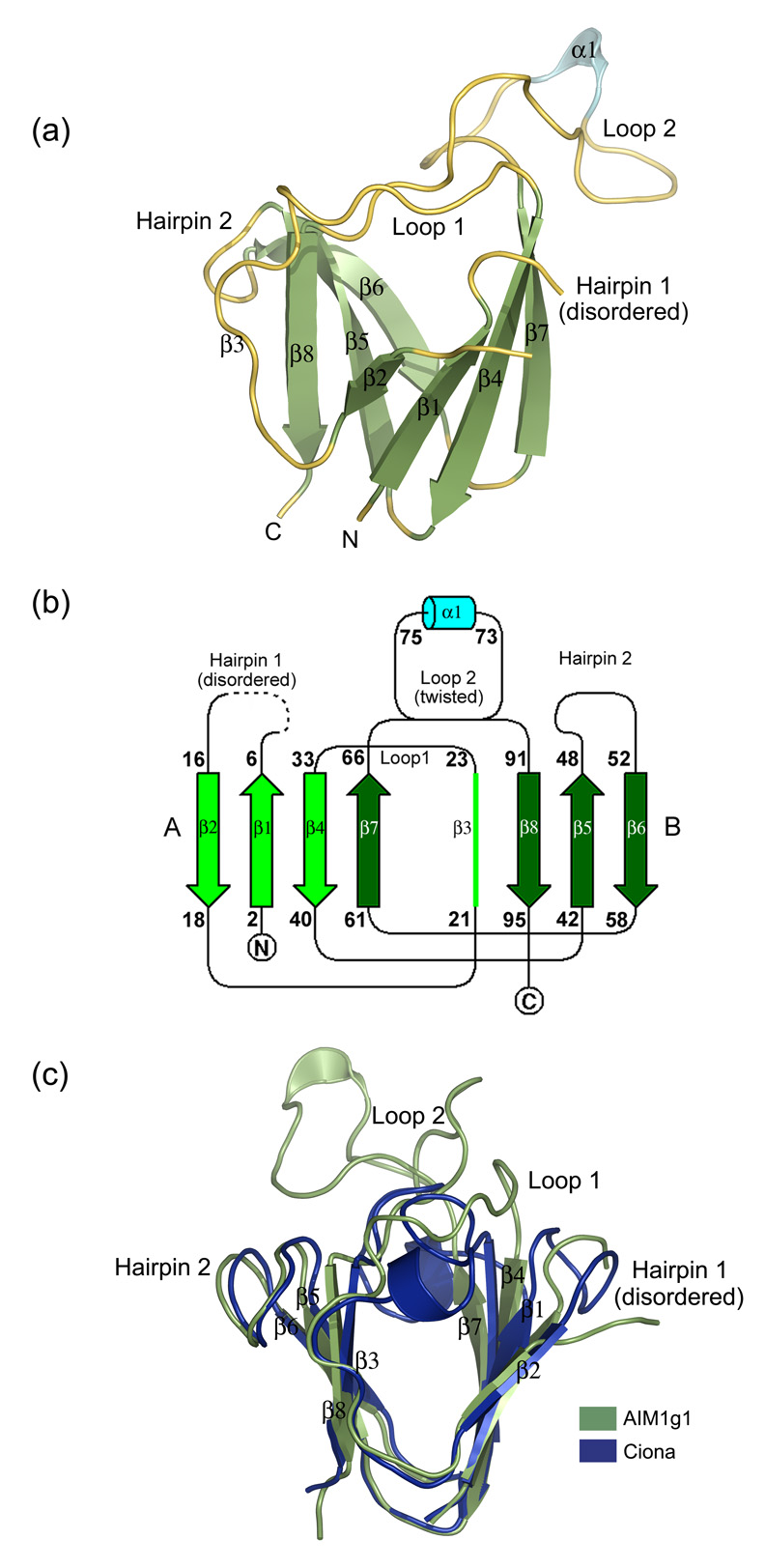
Figure 2.
(a) 3D-structure of the AIM1g1 domain. The secondary structural elements have been marked. The third strand (β3) is marked in spite its loop like appearance for greater clarity as it deviates only partly from the strand architecture and is a conserved feature among all vertebrate βγ-crystallins. (b) Topology of AIM1g1 is depicted which shows the presence of the twin Greek key motifs (A & B) with the large twisted loop 2 connecting β7 and β8. (c) Overlap of γB crystallin and βB2 crystallin N-terminal domains with AIM1g1. Grey indicates the backbone of AIM1g1, cyan represents γB crystallin and magenta represents βB2-crystallin domain. The first hairpin of AIM1g1 is splayed due to disorder. Loop 2 clearly shows completely different orientation as compared to the lens βγ-crystallin domains. Extent of overlap is as per values given in Table 2 for structural relatedness which was analyzed by DaliLite program of EBI.31 The purified protein was crystallized using a 2 µl + 2 µl mixture of protein and a reservoir solution containing 1.3–1.4 M Na citrate, 0.1 M HEPES, pH 7.3–7.5 with non-polar solvents like isopropanol (1–3%), DMSO (2%) and salts like ammonium sulphate (0.06 M), sodium chloride (0.4 M) as additives.32 Different heavy atom compounds like thiomersal, cadmium chloride and sodium iodide were initially attempted by soaking crystals in high concentrations (10–50 mM) of these solutions and observing the crystals for morphological changes. Both time of soak and concentration of the soak were altered to get well diffracting isomorphous derivatives. All derivatized crystals were transferred to 15% glycerol solution containing the heavy atom, before being flash frozen at 100K. Data were collected over large sectors to collect the anomalous signal for the heavy atom especially for iodide derivative, as Iodine is known to have high anomalous signal when CuKα X-rays are used.33 Good derivatives and native data were then scaled together and phasing was performed using the program SOLVE. Solve picked up six sites, three each for Iodine derivative and Cadmium derivative, and yielded a Mean figure of merit (<m>) of 0.51 up to a resolution of 2.1 Å with good electron density maps depicting clear β-strands in the map built without density modification. Density modification and automated model building was done by Resolve which built up to ~80% of the main chain with ~60 % of the side chains. Manual model building was performed using the program ‘O’.