Abstract
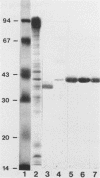
Protein D, a novel surface protein of the bacterial species Haemophilus influenzae with specific affinity for human immunoglobulin (Ig) D was detected in all 127 H. influenzae strains studied. All strains representing different serotypes of encapsulated strains and different biotypes of nonencapsulated strains bound 125I-labeled IgD to a high degree (38 to 74%). Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Western blot (immunoblot) analysis showed that protein D from all H. influenzae strains had the same apparent molecular weight (i.e., 42,000) and reacted with all three different anti-protein D monoclonal antibodies. By Scatchard analysis, the number of protein D residues on a nontypeable H. influenzae strain was estimated to be approximately 2,800 per organism. The equilibrium constant for the reaction between a human IgD myeloma protein and IgD was found to be 5.8 x 10(8) M-1. Also, all strains of H. haemolyticus and H. aegypticus strains tested bound IgD, 21 to 28% and 41 to 48%, respectively. In extracts of those bacteria, a 42,000-molecular-weight protein reactive with IgD and all three anti-protein D monoclonal antibodies was found. In H. parainfluenzae, H. aphrophilus, H. paraphrophilus, and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, a 42,000-molecular-weight protein that was reactive with one to three of three anti-protein D monoclonal antibodies but not reactive with human IgD was detected with Western blot analysis. Other Haemophilus species (H. ducreyi, H. parasuis, H. parahaemolyticus, H. segnis, and H. haemoglobinophilus) did not react with human monoclonal IgD or anti-protein D antibodies. On the basis of the wide distribution of protein D among H. influenzae strains, we suggest that protein D could be a vaccine candidate.
Full text
PDF


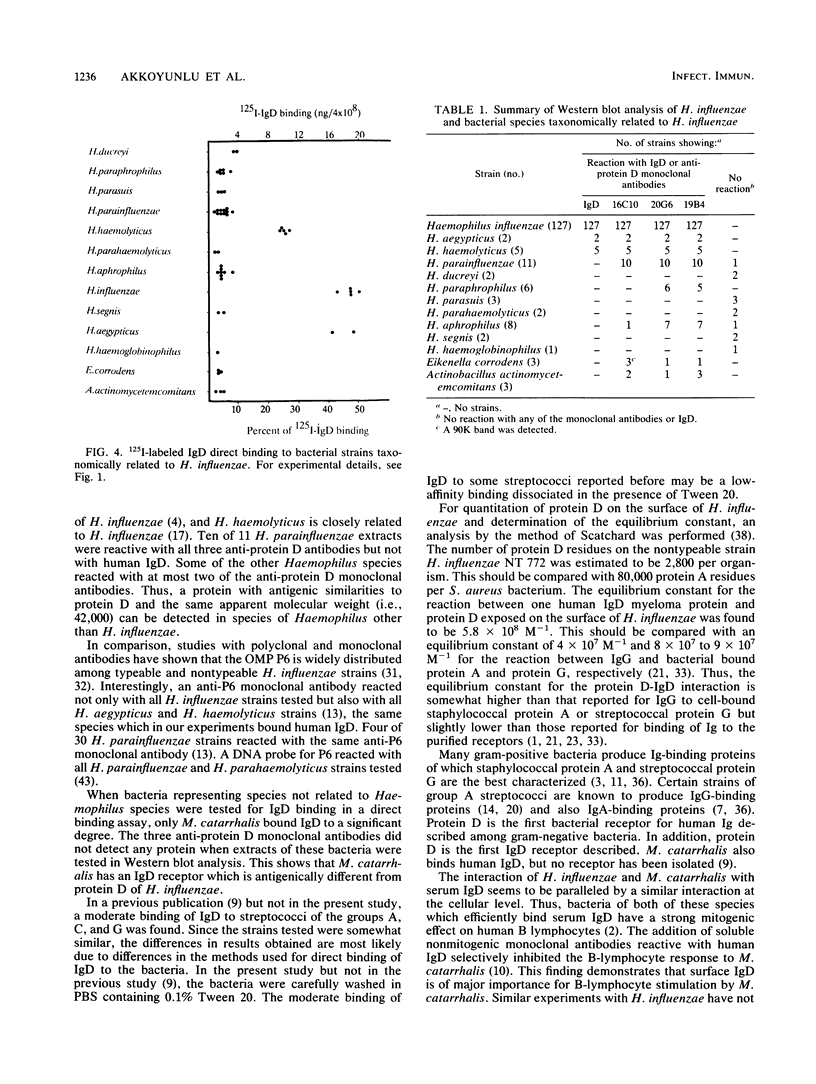


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerström B., Björck L. A physicochemical study of protein G, a molecule with unique immunoglobulin G-binding properties. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10240–10247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURSTEIN M., SAMAILLE J. [On a rapid determination of the cholesterol bound to the serum alpha- and beta-lipoproteins]. Clin Chim Acta. 1960 Jul;5:609–609. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(60)90075-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banck G., Forsgren A. Many bacterial species are mitogenic for human blood B lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(4):347–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00528.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björck L., Kronvall G. Purification and some properties of streptococcal protein G, a novel IgG-binding reagent. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):969–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J. J., Kirkegaard E., Korner B. Haemophilus isolated from unusual anatomical sites. Scand J Infect Dis. 1990;22(4):437–444. doi: 10.3109/00365549009027075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Grubb A. O. Many bacterial species bind human IgD. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1468–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Penta A., Schlossman S. F., Tedder T. F. Branhamella catarrhalis activates human B lymphocytes following interactions with surface IgD and class I major histocompatibility complex antigens. Cell Immunol. 1988 Mar;112(1):78–88. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90277-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff D. M., Osterholm M. T. Safety and efficacy of Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide vaccine. Pediatrics. 1987 Oct;80(4):590–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeneveld K., van Alphen L., van Ketel R. J., Geelen-van den Broek L., Eijk P. P., Zanen H. C. Nonculture detection of Haemophilus influenzae in sputum with monoclonal antibodies specific for outer membrane lipoprotein P6. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2263–2267. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2263-2267.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb A., Grubb R., Christensen P., Schalén C. Isolation and some properties of an IgG Fc-binding protein from group A streptococci type 15. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1982;67(4):369–376. doi: 10.1159/000233049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janson H., Hedén L. O., Grubb A., Ruan M. R., Forsgren A. Protein D, an immunoglobulin D-binding protein of Haemophilus influenzae: cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):119–125. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.119-125.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. G. Agarose gel electrophoresis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:7–19. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M. A taxonomic study of the genus Haemophilus, with the proposal of a new species. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Mar;93(1):9–62. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A surface component in group A, C, and G streptococci with non-immune reactivity for immunoglobulin G. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1401–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Quie P. G., Williams R. C., Jr Quantitation of staphylococcal protein A: Determination of equilibrium constant and number of protein A residues on bacteria. J Immunol. 1970 Feb;104(2):273–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl G., Akerström B. Receptor for IgA in group A streptococci: cloning of the gene and characterization of the protein expressed in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Feb;3(2):239–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb01813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R. Protection of infant rats from Haemophilus influenzae type b infection by antiserum to purified outer membrane protein a. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2612–2618. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2612-2618.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Zachary A. L., Smith D. H. Isolation and partial characterization of outer and inner membranes from encapsulated Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):596–604. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.596-604.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen J. H., Tauber I., Leeuwenberg A. D., Beckers P. J., Sieben M. Parasitologic and serologic observations of infection with Pneumocystis in humans. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Purification and partial characterization of outer membrane proteins P5 and P6 from Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):544–549. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.544-549.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R. S., Jr, Shenep J. L., Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M. Purification and comparison of outer membrane protein P2 from Haemophilus influenzae type b isolates. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):677–684. doi: 10.1172/JCI111017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: a review of clinical aspects, surface antigens, and the human immune response to infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C., Campagnari A. A., Nelson M. B., Apicella M. A. Antigenic characterization of the P6 protein of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):774–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.774-779.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Nelson M. B., Dudas K. C., Mylotte J. M., Apicella M. A. Identification of a specific epitope of Haemophilus influenzae on a 16,600-dalton outer membrane protein. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1300–1307. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B., Kronvall G. Immunochemical aspects of Fc-medicated binding of human IgG subclasses to group A, C and G streptococci. Mol Immunol. 1980 Dec;17(12):1563–1573. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90182-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltola H., Käyhty H., Virtanen M., Mäkelä P. H. Prevention of Hemophilus influenzae type b bacteremic infections with the capsular polysaccharide vaccine. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 14;310(24):1561–1566. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406143102404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redmond S. R., Pichichero M. E. Hemophilus influenzae type b disease. An epidemiologic study with special reference to day-care centers. JAMA. 1984 Nov 9;252(18):2581–2584. doi: 10.1001/jama.252.18.2581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis K. J., Ayoub E. M., Boyle M. D. Streptococcal Fc receptors. I. Isolation and partial characterization of the receptor from a group C streptococcus. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3091–3097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruan M. R., Akkoyunlu M., Grubb A., Forsgren A. Protein D of Haemophilus influenzae. A novel bacterial surface protein with affinity for human IgD. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3379–3384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Robbins J. B., Parke J. C., Jr, Bell C., Schlesselman J. J., Sutton A., Wang Z., Schiffman G., Karpas A., Shiloach J. Quantitative and qualitative analyses of serum antibodies elicited in adults by Haemophilus influenzae type b and pneumococcus type 6A capsular polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugates. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):519–528. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.519-528.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppälä I., Sarvas H., Mäkelä O., Mattila P., Eskola J., Käyhty H. Human antibody responses to two conjugate vaccines of Haemophilus influenzae type B saccharides and diphtheria toxin. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Oct;28(4):471–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb01478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro E. D., Capobianco L. A., Berg A. T., Zitt M. Q. The immunogenicity of Hemophilus influenzae type B polysaccharide-Neisseria meningitidis group B outer membrane protein complex vaccine in infants and young children. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):1064–1067. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Terada T. Removal of dodecyl sulfate from protein solution. Anal Biochem. 1988 Jul;172(1):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90440-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorell J. I., Larsson I. Lactoperoxidase coupled to polyacrylamide for radio-iodination of proteins to high specific activity. Immunochemistry. 1974 Apr;11(4):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(74)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de StGroth S. F., Scheidegger D. Production of monoclonal antibodies: strategy and tactics. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(1-2):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]