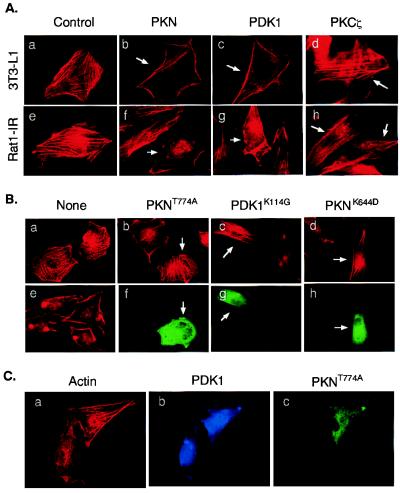
Figure 4.
Effects of PDK1 and PKN on actin cytoskeleton reorganization. (A) Ectopic expression of PDK1 and PKN induces actin cytoskeleton reorganization. 3T3-L1 (Upper) or Rat1-IR (Lower) cells were transfected with plasmids encoding FLAG-PKN, myc-PDK1, or myc-PKCζ, respectively. Arrows indicate cells expressing the recombinant proteins as determined by staining with antibodies to the tags. Actin cytoskeleton was detected by a rhodamine-phalloidin stain. (B) Ectopic expression of mutant PKN or PDK1 blocks insulin-induced actin cytoskeleton reorganization. Rat1-IR cells (a and e) or cells transiently expressing FLAG-PKNT774A (b and f), myc-PDK1K114G (c and g), or FLAG-PKNK644D (d and h) were serum starved for 4 h and treated with 10 nM insulin for 10 min (b–h). Actin cytoskeleton was detected by a rhodamine-phalloidin stain (a–e). The expression of the recombinant proteins in cells was determined by staining with the anti-FLAG or anti-myc antibodies, followed by Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse Ig (f–h). Images are representative of those in three independent experiments. (C) Overexpression of PKNT774A inhibits PDK1-induced actin stress fiber reorganization. Rat1-IR cells were cotransfected with FLAG-tagged PKNT774A and myc-tagged PDK1. The expression of the recombinant proteins in cells was determined by staining with the anti-FLAG or anti-myc antibodies, followed by Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse Ig (green, for PKNT774A) or Alexa Fluor 350-conjugated goat anti-rabbit Ig (blue, for PDK1), respectively. Actin cytoskeleton was detected by a rhodamine-phalloidin stain (red). Results are representative of two independent experiments in which the inhibition of PDK1-induced actin stress fiber reorganization was observed in approximately 65% of cells coexpressing PKNT774A.