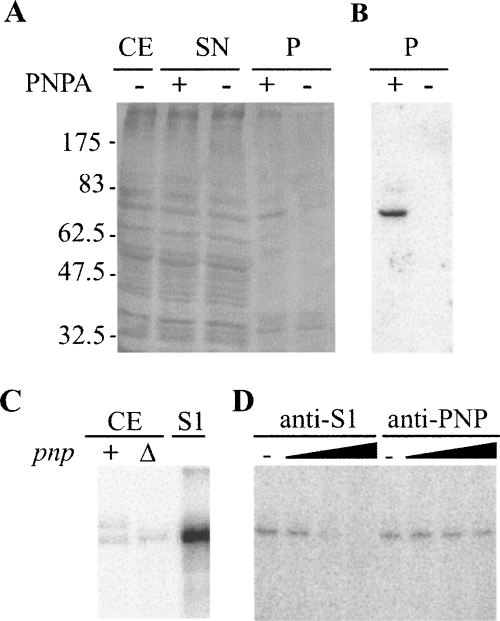
FIGURE 2.
Identification of PLBP as the ribosomal protein S1. (A,B) Affinity purification of PLBP. (A) Aliquots of fractions obtained from C-5691 during the purification procedure detailed in Materials and Methods section were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and silver stained. (CE) crude extract (2 μg); (SN) supernatant fraction recovered after centrifugation of the mix between crude extract and streptavidin-coated beads (2 μg); (P) fraction eluted from the beads (one third of the elution volume); (−), fraction eluted from mock beads. Molecular weight of protein markers is indicated on the left. (B) Northwestern analysis. Ten microliters of P samples were run on 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel, blotted onto a nitrocellulose sheet, and incubated with radiolabeled PNPA substrate. (C,D) S1 binding to PNPA in UV-crosslinking assays. (C) Crosslinking with crude cell extracts. We incubated 5 × 104 cpm of [32P]-labeled PNPA with 0.3 μg of C-5612/pAZ8 (+) or C-5691 (Δ) crude extract or with 1 pmol of purified S1 and UV-irradiated as detailed in Materials and Methods. The reaction products were then separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, blotted onto a nitrocellulose filter, and visualized by phosphorimaging. (D) Cross-linking with S1-immunodepleted cell extracts. We cross-linked 0.3 μg of C-1a crude extract preincubated 30 min at 37°C without (−) or with different amounts of S1 (1, 10, 100 μg) or PNPase (0.165, 1.65, 16.5 μg) antiserum to radiolabeled PNPA and analyzed it as described in C.