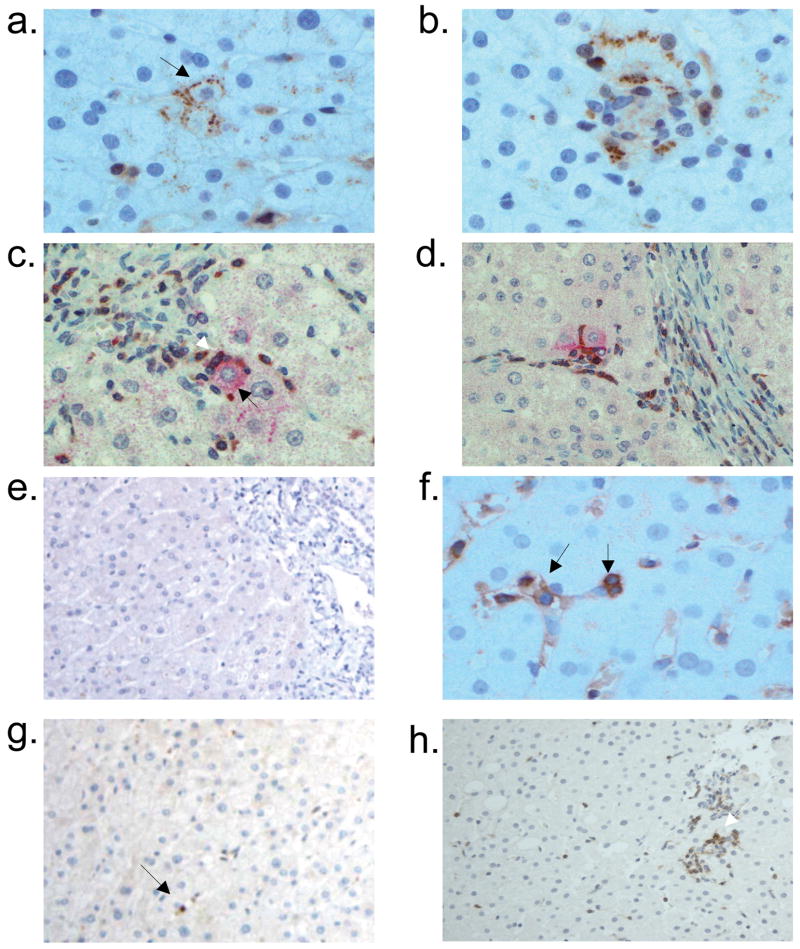
Figure 5.
Hepatic parenchymal expression of monokine induced by interferon γ (Mig/CXCL9) and interferon inducible T-cell alpha chemoattractant (I-TAC/CXCL11) in chronic hepatitis C virus infection and an uninfected individual. CXCL9 is detected primarily in a) lobular hepatocytes (black arrow; x400). b) CXCL9-stained hepatocytes are localized in an area with heavy lymphocyte infiltration (x400). Dual immunostaining with anti-CXCL9 (red) and anti-CXCR3 (brown) in c) parenchyma (x400) and d) periportal (x200) areas reveal co-localization of CXCL9+ hepatocytes (black arrow in c) with CXCR3+ lymphocytes (white arrow in c). e) CXCL9 is not detected in a liver specimen from an uninfected individual (x200). f) CXCL11 is observed primarily on sinusoidal endothelial cells (left arrow) and lobular lymphocytes (right arrow; x400). g) In uninfected liver, CXCL11 staining was detected on an occasional lymphocyte (black arrow; x200). h) CXCR3 is detected on the majority of lobular lymphocytes (white arrow; x100). i) CXCR3-expressing lymphocytes were not detected in uninfected liver.