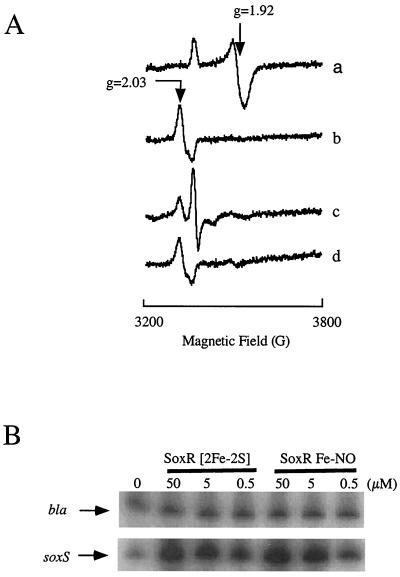
Figure 4.
Properties and activity of re-purified, NO-treated SoxR. (A) EPR spectroscopy. Purified SoxR protein (23, 33) (2.5 ml, 3 μM) was mixed with 100 μl of a NO-saturated solution in water. The NO-treated protein was then reduced with sodium dithionite (20 mM), followed by reoxidation with 1 mM potassium ferricyanide. Trace a, dithionite-reduced, purified SoxR; trace b, NO-treated SoxR, showing d7 signal; trace c, NO-treated SoxR reduced with dithionite, showing d9 signal; trace d, reoxidation of protein from trace c. A small signal at ≈3,500 G may be attributable to dithionite, as it persists in the reoxidized sample (compare traces c and d). (B) In vitro transcription by NO-treated SoxR. In vitro transcription reactions (23, 24) used the indicated amounts of purified, oxidized SoxR (SoxR [2Fe-2S]), or purified, NO-treated SoxR (SoxR Fe-NO). The transcripts were quantified by primer extension (40). bla, SoxR-independent transcript; soxS, transcript from the SoxR-dependent soxS gene.