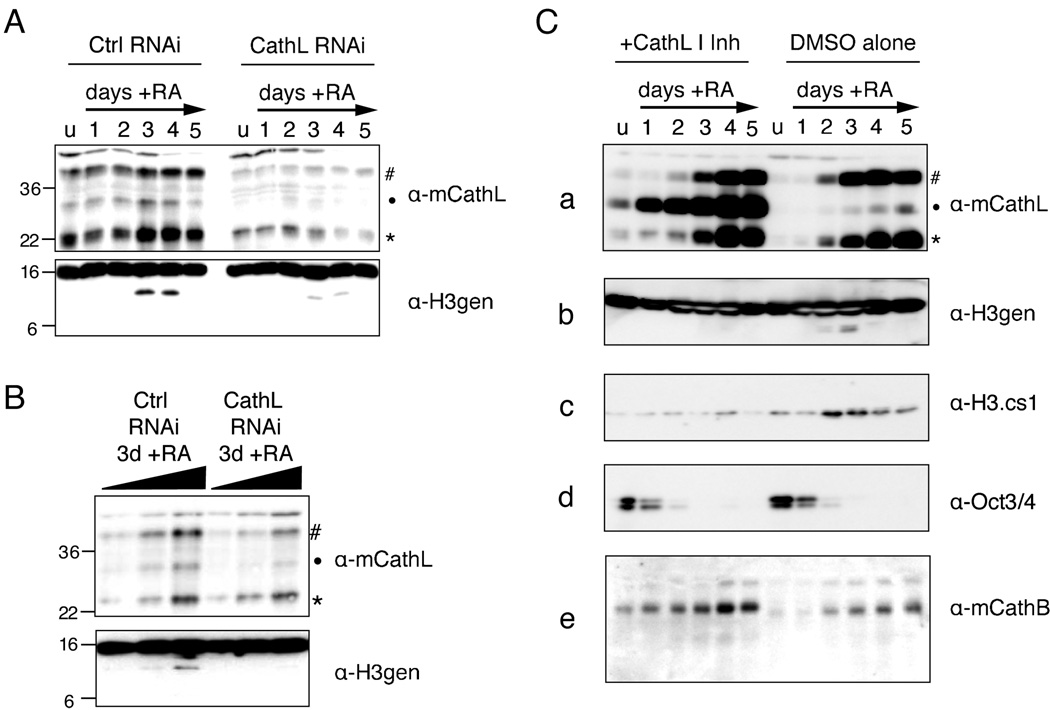
Figure 6. Both RNAi and chemical inhibition of Cathepsin L reduce histone H3 cleavage in vivo.
(A) Control and Ctsl RNAi cells lines were differentiated with RA as usual and harvested at the indicated time points; WCEs were then separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed for both Cathepsin L expression (upper panel) and histone H3 cleavage (lower panel) by immunoblotting.
(B) A serial two-fold dilution of samples from day 3 post-induction with RA were resolved by SDS-PAGE gel and analyzed by immunoblotting as in (A).
(C) The addition of Cathepsin L Inhibitor I to the cell media of differentiating ESCs (left side) inhibits the processing of Cathepsin L itself (a) as well as that of histone H3 (b, c) as compared to DMSO alone treated control cells (right side). Loss of pluripotency marker Oct 3/4 was not affected (d) nor was the self-processing of another cathepsin family member, Cathepsin B (e).