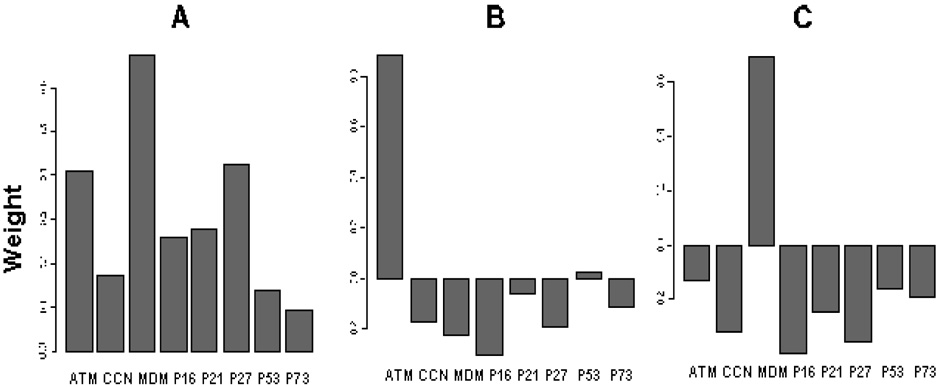
Figure 5.
Principal component analysis. A, first component; B, second component; C, third component. Each principal component is a weighted sum of the concentrations of the eight proteins. The weights (shown on y-axes) in each principal component form a unit-length vector, which means the sum of the squares of the weights is equal to one. These three principal components form three vectors that are perpendicular to each other in the eight-dimensional space, i.e., these vectors are linearly independent of each other.29