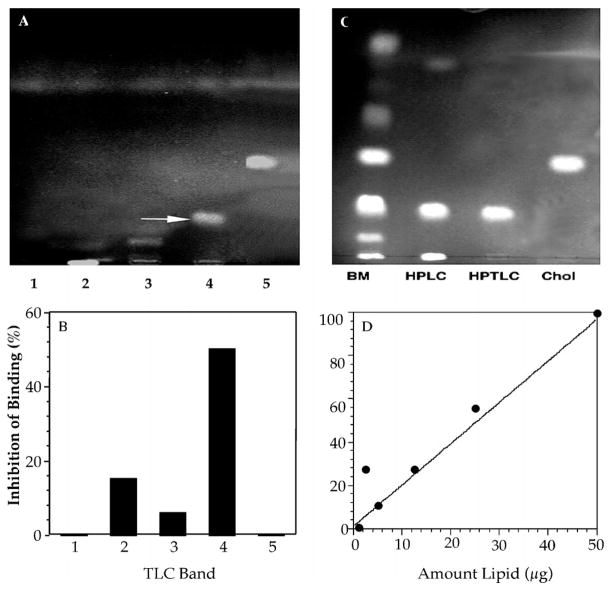
Figure 8.
Purification of sporozoite-binding inhibitory component in bovine mucosa. Organic solvent extracts of bovine mucosa were separated by HPLC and active fractions chromatographed on TLC plates using chloroform:methanol (30:1) as the solvent. Individual bands were scraped from the plates and eluted with chloroform:methanol:water (30:60:20), evaluated for purity and sporozoite-binding inhibitory activity. A. Aliquots of the eluate rechromatographed on analytical TLC plates. B. Aliquots of each eluted TLC band from the plate shown in panel A were tested for inhibitory activity in the standard binding assay (note band 4 contained the majority of the inhibitory activity). C. Band 4 rechromatographed on analytical HPTLC plates developed in chloroform:methanol (30:1) and compared with the starting bovine mucosal extract (BM), active HPLC fraction (HPLC), HPTLC purified band 4 (HPTLC), and cholesterol standard (Chol). Negative controls: areas of each lane, where no stained band was apparent, as well as entire blank lanes and cholesterol bands were scraped, extracted, and tested in the sporozoite-binding assay. None of this fraction exhibited sporozoite-binding inhibitory activity. D. Effect of increasing amounts (μg) of purified band 4 on inhibition of sporozoite binding.