Figure 2.
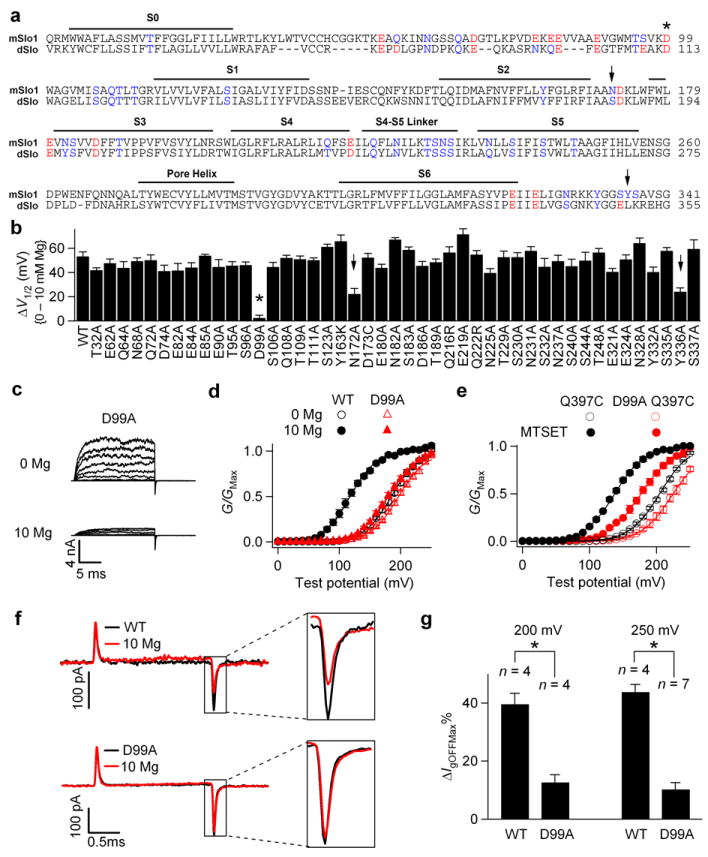
D99A abolishes Mg2+ sensitivity by preventing Mg2+ binding. (a) Sequence alignment of the membrane-spanning (TM) domain in mSlo1 and dSlo channels. Mutations of the oxygen-containing residues that are conserved between mSlo1 and dSlo and potentially face cytosol (red and blue colors) were tested. mSlo1: (mouse, GI: 347143); dSlo: (drosophila, GI: 115311626). (b) Shifts of the G-V relationship induced by 10 mM [Mg2+]i for WT and the mutations. (c) Macroscopic current traces of D99A in 0 and 10 mM [Mg2+]i. Testing potentials were from -20 to 240 mV with 20-mV increments. Both holding and repolarizing potentials were -80 mV. (d) G-V relationship for WT and D99A. (e) Mean G-V relationship of Q397C and D99A Q397C channels before (hollow) and after (filled) 200 μM MTSET treatment. For all the experiments with MTSET treatment in this study, C430A was used as background to remove the endogenous MTSET effect on channel activation14,36. (f) Gating current (Ig) traces for WT (upper panel) and D99A mutant (lower panel) channels with (red) and without (black) 10 mM [Mg2+]i in response to a 2-ms, 250 mV depolarizing pulse. Ig traces of the same patch were first recorded in the absence of Mg2+, and then 10 mM [Mg2+]i. (g) Effects of 10 mM [Mg2+]i on the reduction of peak OFF gating currents (IgOFFMax) in response to 2-ms, 200 mV or 250 mV depolarizing pulses.ΔIgOFFMax%= (IgOFFMax(0Mg)-IgOFFMax(10Mg))/IgOFFMax(0Mg). * indicates p≤0.001.
