Figure 5. Acute blockade of Arc translation blocks the long-term effects of mGluR activation on GluR1 trafficking.
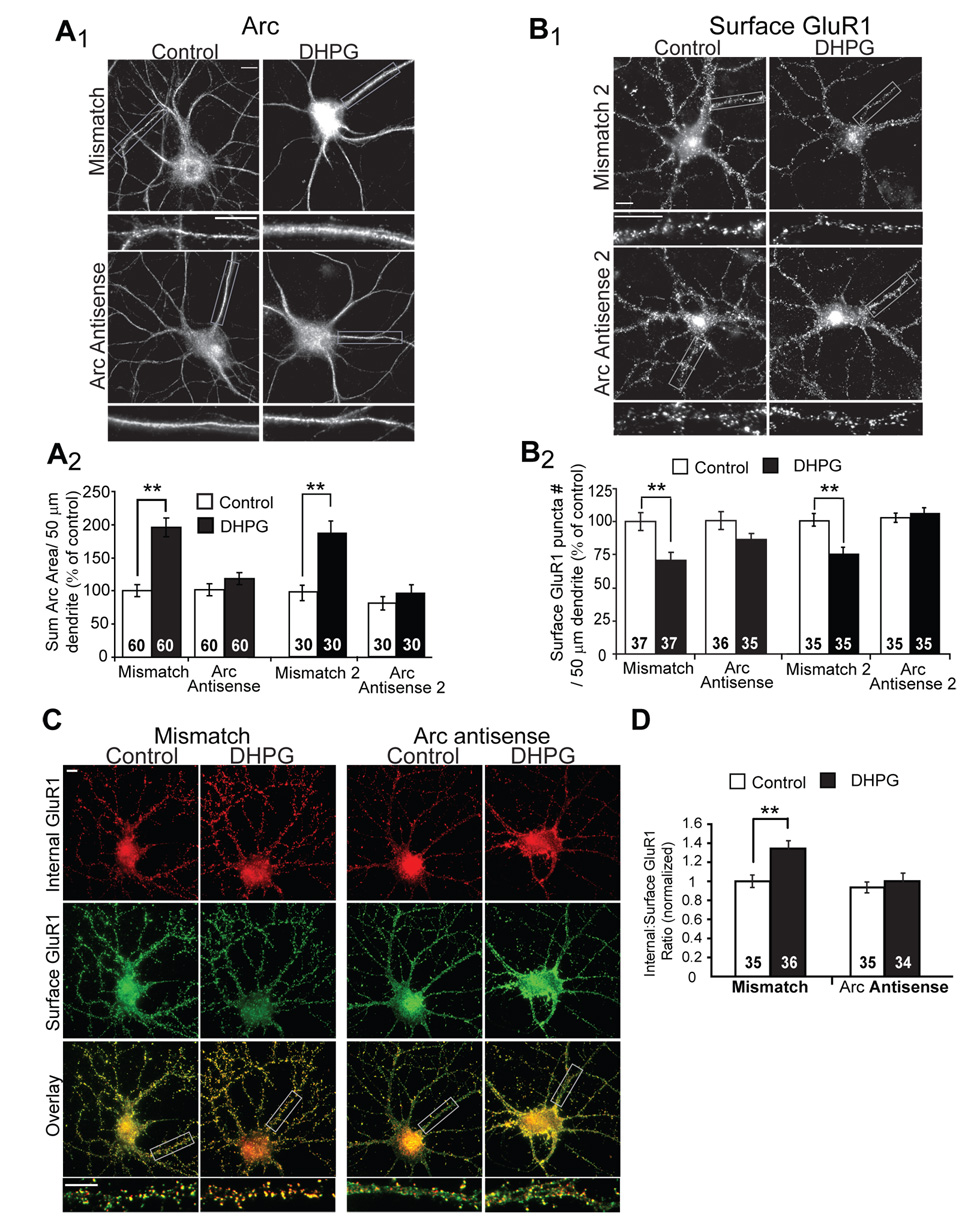
A1, Representative images of Arc immunofluorescence in dissociated hippocampal neurons. Antisense oligonucleotides directed against Arc mRNA, or mismatch oligonucleotides were introduced into 19–21 DIV neurons via a lipid-based delivery system. Neurons were treated with media (control) or DHPG and fixed 10 min after onset of treatment. A2, Quantification of the area of the dendritic Arc fluorescence reveal that either one of two unique Arc antisense oligonucleotides (Arc antisense and Arc antisense 2) block DHPG-induced increases in Arc protein without affecting basal Arc levels (in control mismatch oligo treated cultures). Data from 2 cultures per condition. B1, Representative images of surface GluR1 in neurons treated with antisense or mismatch oligonucleotides 30 min prior to media (control) or DHPG treatment. One hour after DHPG, neurons were fixed and processed for surface GluR1 immunofluorescence. B2, Quantified group data reveal that DHPG fails to induce long-term decreases in surface GluR1 in neurons pretreated with either Arc antisense oligonucleotides, in contrast to neurons treated with mismatch oligonucleotides. Data from 2–3 cultures/condition. C, Representative double-label images of surface (green) and internalized (red) GluR1 in dissociated hippocampal neurons treated with Arc antisense oligo or mismatch oligo. One hour after media (control) or DHPG treatment (100 µM, 5 min), live neurons were labeled with GluR1 antibody. D, Ratiometric quantification of internal to surface GluR1 in the same dendrites reveal that Arc antisense oligonucleotide blocks DHPG-induced, long-term increases in GluR1 endocytosis rate. Data from 2 cultures per condition. In all images scale bars = 10 µm.
