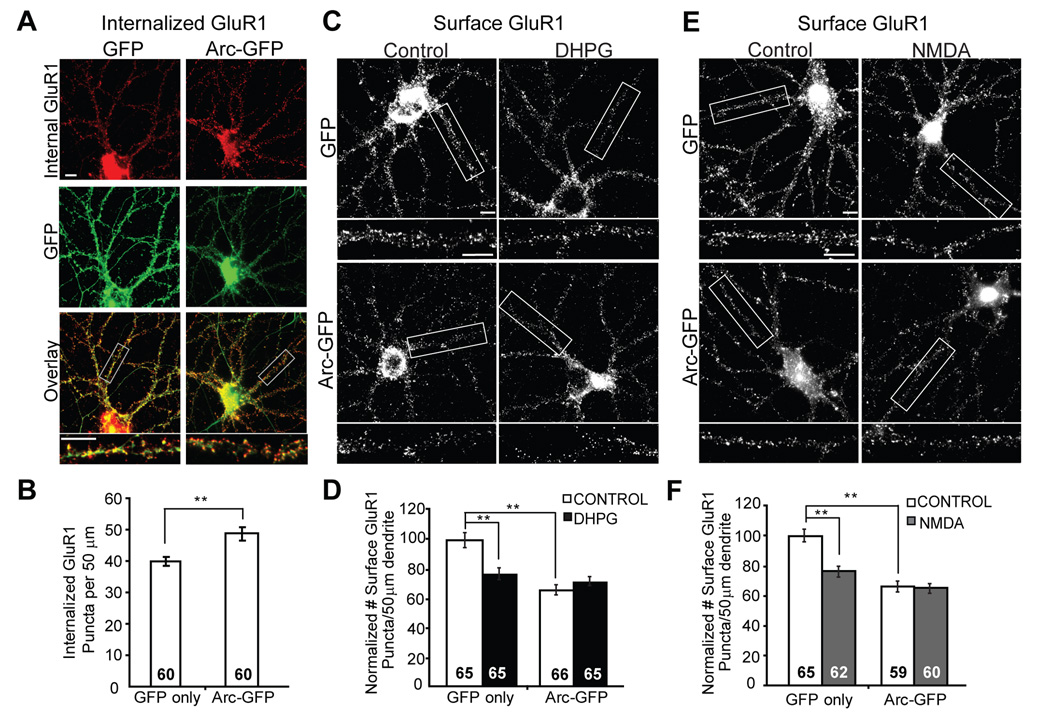
Figure 7. Overexpression of Arc in hippocampal neurons increases GluR1 endocytosis and occludes mGluR induced decreases in surface GluR1.
A, Representative immunofluorescence of internalized GluR1 in hippocampal neurons infected with lentivirus containing GFP or Arc-GFP (green). B, Quantification of internalized GluR1 puncta reveal that neurons with Arc-GFP expression have increased GluR1 endocytosis rate as compared to neurons expressing GFP only. Data from 3 cultures. C, Representative images of surface GluR1 staining in neurons infected with lentivirus containing GFP or Arc-GFP. Neurons were treated with media (control) or DHPG (100 µM, 5 min) and fixed one hour after onset of treatment. D, Quantification of surface GluR1 puncta number in GFP or Arc-GFP infected neurons treated with media (control) or DHPG reveal that Arc-GFP overexpression decreases basal surface GluR1 levels and blocks DHPG-induced decreases in surface GluR1. Data from 3 cultures. E, Representative images of surface GluR1 staining in neurons infected with lentivirus containing GFP or Arc-GFP. Neurons were treated with media (control) or NMDA and fixed one hour after onset of treatment. F, Quantification of surface GluR1 puncta number in GFP or Arc-GFP infected neurons treated with media (control) or NMDA reveal that Arc-GFP overexpression decreases basal surface GluR1 levels and blocks NMDA-induced decreases in surface GluR1. Data from 3 cultures. In all images scale bars = 10 µm.