Abstract
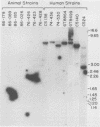
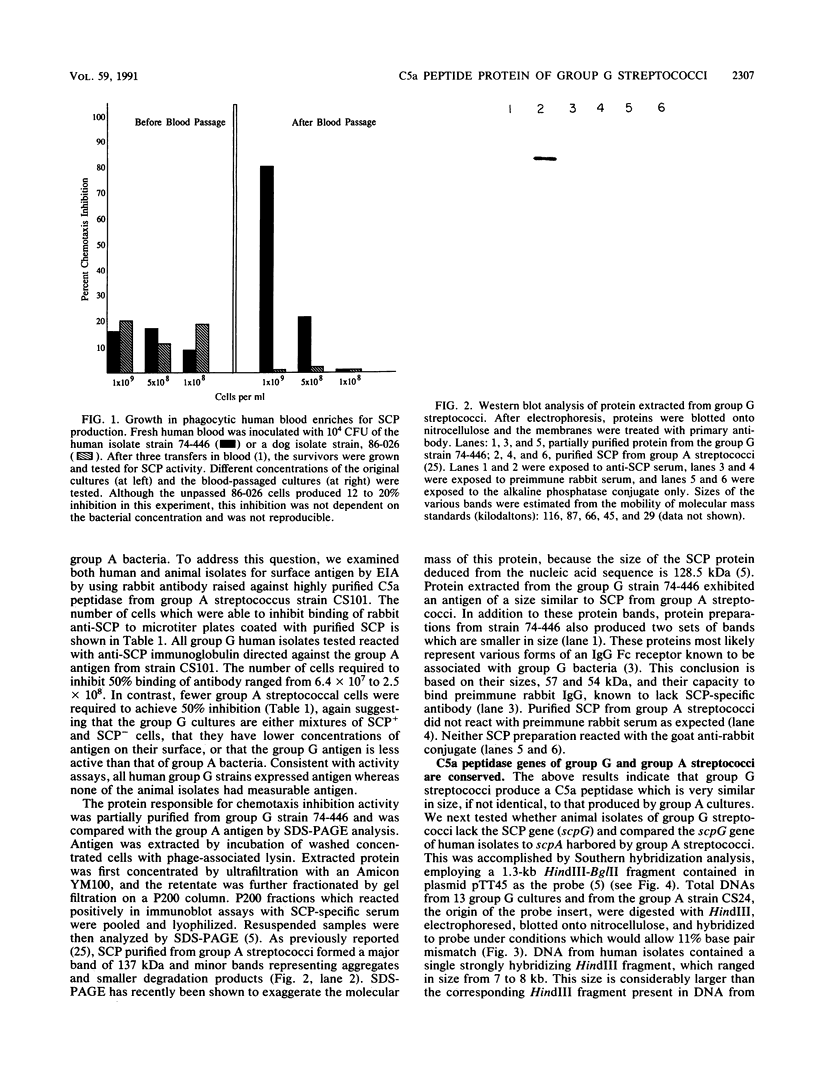
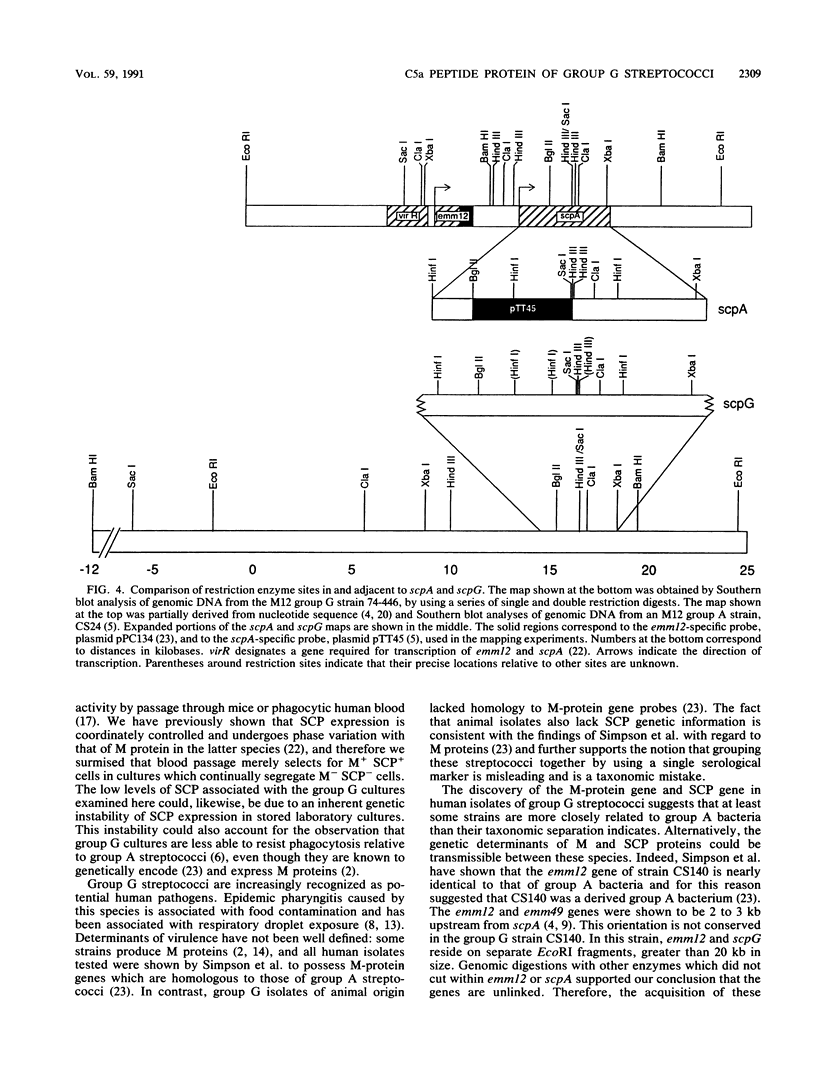
Specific proteolytic destruction of the human chemotaxin, C5a, is a property of group A and B streptococcal pathogens. Here we show that virulent group G streptococci from human sources also express C5a peptidase activity. The enzyme responsible for this activity is approximately the same size as and is antigenically similar to that produced by group A streptococci. On the basis of Southern hybridization analysis with an internal fragment of the group A C5a peptidase gene (scpA) as a probe, a copy of this gene was found in the genome of all group G human isolates tested. Comparison of partial restriction maps of scpA and scpG revealed significant similarity between the two genes. Group G strains isolated from dogs and cows were found to lack C5a peptidase activity and did not hybridize to the scpA-specific probe. The association of this activity with three streptococcal species suggests that elimination of phagocyte chemotactic attractants is a more universal virulence mechanism than originally anticipated.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECKER C. G. SELECTION OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI RICH IN M-PROTEIN FROM POPULATIONS POOR IN M-PROTEIN. Am J Pathol. 1964 Jan;44:51–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisno A. L. Alternate complement pathway activation by group A streptococci: role of M-protein. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1172–1176. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1172-1176.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björck L., Kastern W., Lindahl G., Widebäck K. Streptococcal protein G, expressed by streptococci or by Escherichia coli, has separate binding sites for human albumin and IgG. Mol Immunol. 1987 Oct;24(10):1113–1122. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. C., Cleary P. P. Cloning and expression of the streptococcal C5a peptidase gene in Escherichia coli: linkage to the type 12 M protein gene. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1740–1745. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1740-1745.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. C., Cleary P. P. Complete nucleotide sequence of the streptococcal C5a peptidase gene of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3161–3167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. O., Gross H., Harrell W. K. Immunogenicity and characteristics of M protein released by phage-associated lysin from group-A streptococci types 1 and 23. J Med Microbiol. 1977 May;10(2):179–194. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haanes E. J., Cleary P. P. Identification of a divergent M protein gene and an M protein-related gene family in Streptococcus pyogenes serotype 49. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6397–6408. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6397-6408.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. R., Bohnsack J. F., Morris E. Z., Augustine N. H., Parker C. J., Cleary P. P., Wu J. T. Group B streptococci inhibit the chemotactic activity of the fifth component of complement. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3551–3556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horstmann R. D., Sievertsen H. J., Knobloch J., Fischetti V. A. Antiphagocytic activity of streptococcal M protein: selective binding of complement control protein factor H. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1657–1661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks-Weis J., Kim Y., Cleary P. P. Restricted deposition of C3 on M+ group A streptococci: correlation with resistance to phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1897–1902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOODY M. D., PADULA J., LIZANA D., HALL C. T. EPIDEMIOLOGIC CHARACTERIZATION OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI BY T-AGGLUTINATION AND M-PRECIPITATION TESTS IN THE PUBLIC HEALTH LABORATORY. Health Lab Sci. 1965 Jul;2:149–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin N. J., Kaplan E. L., Gerber M. A., Menegus M. A., Randolph M., Bell K., Cleary P. P. Comparison of epidemic and endemic group G streptococci by restriction enzyme analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1881–1886. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1881-1886.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxted W. R., Potter E. V. The presence of type 12 M-protein antigen in group G streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Oct;49(1):119–125. doi: 10.1099/00221287-49-1-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. P., Cleary P. P. In vivo Streptococcus pyogenes C5a peptidase activity: analysis using transposon- and nitrosoguanidine-induced mutants. J Infect Dis. 1987 Sep;156(3):495–504. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.3.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. P., Cleary P. P. Localization of the streptococcal C5a peptidase to the surface of group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):432–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.432-434.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. P., Darip D., Fraley K., Nelson C. M., Kaplan E. L., Cleary P. P. The human antibody response to streptococcal C5a peptidase. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;163(1):109–116. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut A. G. The IgA1 proteases of pathogenic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:603–622. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.003131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. C., Spanier J. G., Jones S. J., Simpson W. J., Cleary P. P. Streptococcus pyogenes type 12 M protein gene regulation by upstream sequences. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5633–5640. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5633-5640.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Cleary P. P. Expression of M type 12 protein by a group A streptococcus exhibits phaselike variation: evidence for coregulation of colony opacity determinants and M protein. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2448–2455. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2448-2455.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., LaPenta D., Chen C., Cleary P. P. Coregulation of type 12 M protein and streptococcal C5a peptidase genes in group A streptococci: evidence for a virulence regulon controlled by the virR locus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):696–700. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.696-700.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Robbins J. C., Cleary P. P. Evidence for group A-related M protein genes in human but not animal-associated group G streptococcal pathogens. Microb Pathog. 1987 Nov;3(5):339–350. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanier J. G., Jones S. J., Cleary P. Small DNA deletions creating avirulence in Streptococcus pyogenes. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):935–938. doi: 10.1126/science.6089334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler D. E., Cleary P. P. Purification and characteristics of the streptococcal chemotactic factor inactivator. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):757–764. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.757-764.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler D. E., Nelson R. D., Cleary P. P. Human neutrophil chemotactic response to group A streptococci: bacteria-mediated interference with complement-derived chemotactic factors. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):239–246. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.239-246.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]