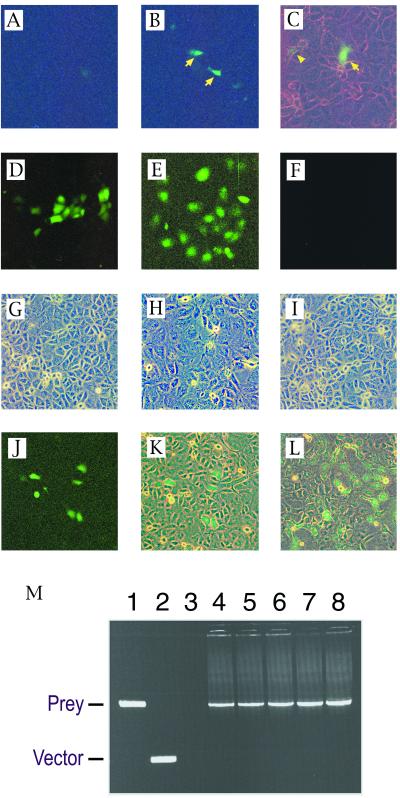
Figure 3.
Recovery of a model prey (MSG1) plasmid from GB133 cells stably expressing a model bait (GAL4DB-Smad4). (A–C) Cells were transiently transfected with a prey (B and C) or empty vector (A), followed by evaluation of GFP expression by fluorescence microscopy at 48 h after transfection (fluorescent light only in A and B; fluorescent light plus weak white light in C). Arrows indicate strongly green fluorescent cells; arrowhead indicates a weakly green fluorescent cell. (D–I) Maintenance of OriP-harboring plasmid in bait-expressing GB133 cells. Expression plasmids for a GAL4DB-fusion transactivating domain with (E) or without (D and F) harboring the OriP replication origin sequence were transiently transfected into the bait-expressing GB133 cells, and expression of GFP was evaluated at 48 h (D) or at 7 days (E and F) after transfection. (G–I) Phase contrast images of cell monolayers corresponding to fluorescence images of D–F are shown in panels G–I, respectively. (J and K) Detection of prey diluted with an excess of empty vectors. Cells were transiently transfected with an OriP-containing prey expression plasmid together with a 2,000-fold molar excess of empty vector, followed by evaluation of GFP expression at 7 days after transfection. Single prey-transfected cells divided three times after transfection, forming green fluorescent cell clusters, each of which consisted of six to eight GFP-expressing cells (fluorescent light only in J; fluorescent light plus weak white light in K). (L) A green fluorescent microcolony of prey-transfected cells 3 days after subculture of the GFP-expressing cell clusters shown in J (fluorescent light plus weak white light). (M) Recovery of prey cDNA from green fluorescent microcolonies by PCR using primers that annealed to the vector sequences flanking the insert-cloning site. Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products is shown. Lane 1, positive control amplification from the prey plasmid; lane 2, negative control amplification from empty vector; lanes 3–8, amplification of prey cDNA from total DNA preparations of five independent GFP-expressing microcolonies.