Figure 4.
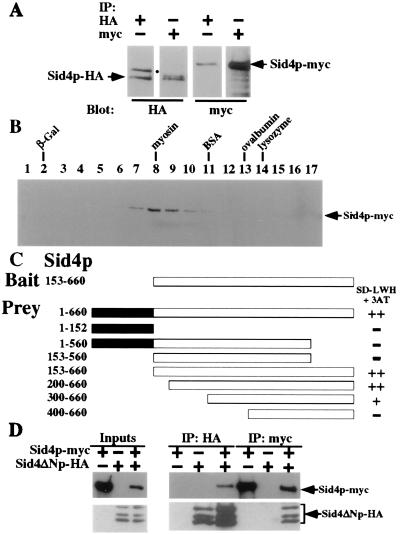
Sid4p interacts with itself. (A) Cell lysates were prepared under native conditions from a sid4-HA/sid4-myc heterozygous diploid strain (KGY2732), immunoprecipitated with either anti-HA or anti-myc, and analyzed by immunoblotting with either anti-HA or anti-myc. The positions of Sid4p-HA and Sid4p-myc are indicated. The position of a nonspecific HA-crossreactive protein is indicated (●). (B) Sid4p-myc sediments with an apparent mass of ≈200 kDa. Cell lysates were prepared under native conditions from a sid4-myc strain (KGY1340) and analyzed by sedimentation in a glycerol gradient. Fraction numbers are indicated. Peak fractions for molecular mass markers sedimented in a parallel gradient are indicated (lysozyme, 14 kDa; ovalbumin, 45 kDa; BSA, 66 kDa; myosin, 220 kDa; β-galactosidase (β-Gal), 464 kDa). (C) Sid4p dimerization domain. Sid4ΔNp in pBI770 (Bait) and Sid4p fragments in pBI771 (Prey) were cotransformed into strain YPB2 (KGY1400) and interactions were analyzed as described in the text. ++, Strong interaction; +, moderate interaction; −, no interaction. The amino acid residues encoded by each fragment are indicated. (D) Sid4p-myc binds directly to Sid4ΔNp-HA. Sid4p-myc and Sid4ΔNp-HA were translated in vitro either separately or together and immunoprecipitated with either anti-HA or anti-myc, and immunopellets were analyzed by immunoblot analysis with either anti-HA or anti-myc. Ten percent of the input into the immunoprecipitation reactions was also resolved by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotted. The positions of Sid4p-myc and Sid4ΔNp-HA (and its internal initiation products) are indicated.