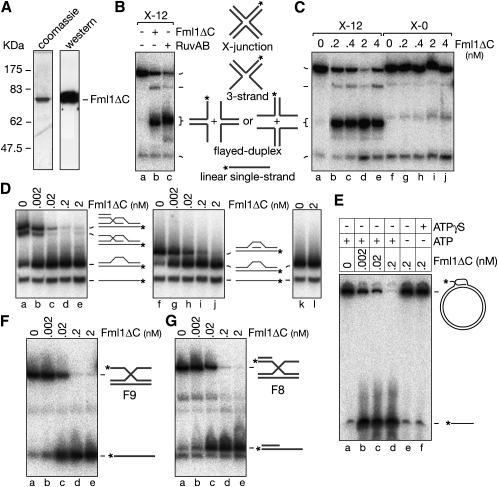
Figure 4.
Catalysis of HJ Branch Migration and D Loop Dissociation by Fml1ΔC
(A) Coomassie blue-stained SDS gel and immunoblot (probed with anti-polyhistidine) showing purified His-tagged Fml1ΔC.
(B) PhosphorImage showing dissociation of X-12 by Fml1ΔC (2 nM) and RuvAB (40 nM RuvA and 630 nM RuvB). The schematic shows the various products of X-junction dissociation. Asterisks indicate 32P label at the DNA 5′ end.
(C) Comparison of the dissociation of X-12 and X-0 by Fml1ΔC.
(D) Dissociation of static D loops by Fml1ΔC. The substrates are D2 (lanes a–e), D7 (lanes f–j), and D8 (lanes k–l). The schematics show the DNA substrates and their various dissociation products, with the asterisks indicating the 32P label at the 5′ end of oligo 16.
(E) Dissociation of a mobile D loop by Fml1ΔC. Reactions were incubated for 15 min at 37°C.
(F and G) Dissociation of the part X-junctions F8 and F9 by Fml1ΔC.