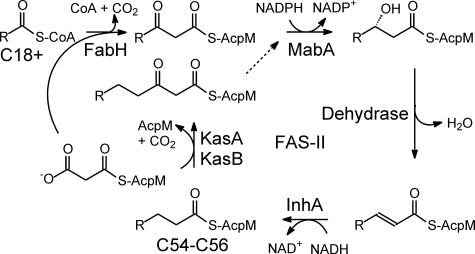
FIGURE 1.
The FAS-II pathway. The FAS-II pathway in M. tuberculosis extends the C18+-CoA products of the FAS-I pathway to C54–C56 fatty acids. The β-ketoacyl synthase FabH condenses the C18+ acyl group with malonyl-AcpM to form a β-ketoacyl-AcpM. This is subsequently reduced, dehydrated, and reduced by the actions of the NADPH-dependent β-ketoacyl reductase MabA, a dehydrase, and the NADH-dependent enoyl reductase InhA, respectively. The β-ketoacyl synthases KasA and KasB initiate additional cycles of elongation by catalyzing the condensation of the growing acyl-AcpM and malonyl-AcpM.