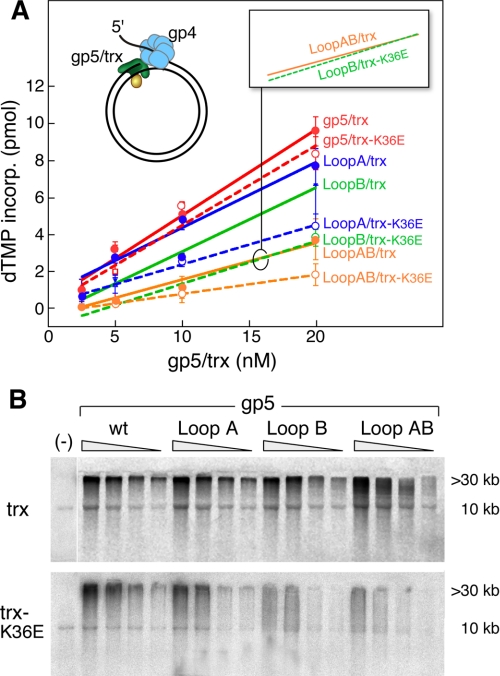
FIGURE 4.
Leading strand DNA synthesis. The ability of gp5/trx complexes and gp4 to catalyze strand displacement DNA synthesis was examined using a circular duplex DNA with a preformed replication fork. A, efficiency of strand displacement DNA synthesis by the complex of trx and trx-K36E with gp5, gp5-loop A, gp5-loop B, and gp5-loop AB was determined. The M13 dsDNA with a replication fork was prepared as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The reaction (10 μl) contained 10 nm DNA template, 40 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 10 mm MgCl2, 5 mm DTT, 50 mm potassium glutamate, and 500 μm each dCTP, dGTP, and dTTP, 0.05 μCi of [α-33P]dATP, 10 nm gp4 (hexamer), 4 μm trx, and 2.5-20 nm of gp5. After 10 min of incubation at 37 °C, the reaction was stopped by EDTA, and the amount of [α-32P]dAMP incorporated into the DNA was measured as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The solid lines represent trx-wt, and broken lines represent trx-K36E. Red lines depict gp5-wt; blue lines depict gp5-loop A; green lines depict gp5-loop B, and yellow lines depict gp5-loop AB. Error bars were derived from two independent experiments. B, products of the reaction described in A were analyzed by electrophoresis on 0.6% alkaline-agarose gel. The products corresponding to the full-length M13 dsDNA (10 kb) and of strand displacement DNA synthesis (>30 kb) are indicated. Synthesis in the absence of gp4 (lane 1) is shown using 20 nm gp5 and 4 μm trx (lane 1). wt, wild type.