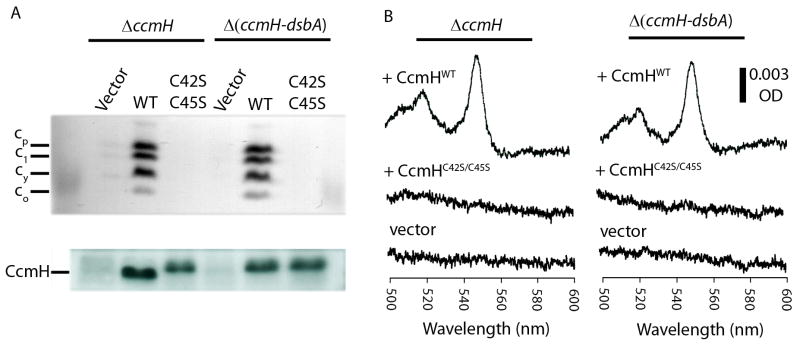
Fig. 5. Cyt c profiles and CcmH immunoblots of wild type and cysteineless CcmH mutants.
Cyts c profiles of R. capsulatus ΔccmH (MD14) and Δ(ccmH-dsbA) (ST27) strains harboring empty plasmid (vector) or wild type (WT/pST6) or cysteineless (C42S C45S/pST14) alleles of ccmH grown in minimal medium were determined by (A) SDS-PAGE/TMBZ analyses (top panel) as in Fig. 2. The same preparations were also subjected to SDS-PAGE using 50 μg total proteins per lane, and the amounts of CcmH were detected by immunoblot analyses (lower panel) using anti-CcmH polyclonal antibodies, as described in Materials and Methods. (B) Cyt c2 levels in the CcmH-null mutant and its DsbA-null derivatives: Ascorbate-reduced minus ferricyanide-oxidized optical difference spectra of soluble fractions (protein concentration of 0.5 mg/ml) obtained from R. capsulatus ΔccmH (left) and Δ(ccmH-dsbA) (right) mutants harboring empty plasmid (vector) or wild type (+ CcmHWT) or cysteineless (+ CcmHC42S/C45S) alleles of ccmH were determined as described in Fig. 2.