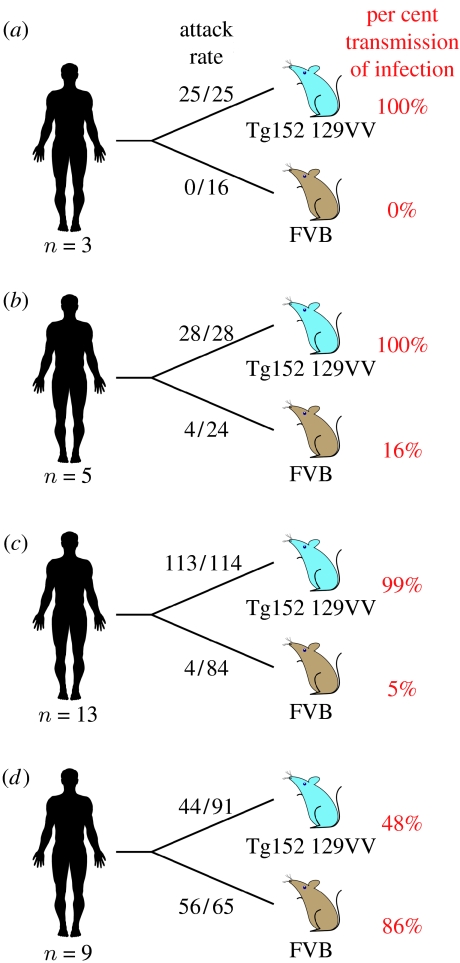
Figure 2.
Summary of rates of transmission of human prions to transgenic and wild-type mice. Brain homogenate from patients with neuropathologically confirmed (a) kuru, (b) iatrogenic CJD, (c) sporadic CJD and (d) variant CJD were inoculated intra-cerebrally into transgenic mice homozygous for a human PrP 129V transgene array and murine PrP null alleles (Prnpo/o) designated Tg(HuPrP129V+/+ Prnpo/o)-152 mice (129VV Tg152 mice; Collinge et al. 1995), and into wild-type FVB/NHsd mice (genotype Prnpa). The number of prion disease isolates examined is designated below each schematic patient. Attack rate is defined as the total number of both clinically affected and sub-clinically infected mice as a proportion of the number of inoculated mice. In mice that were asymptomatic, sub-clinical prion infection was assessed by immunoblotting and/or immunohistochemical examination of brain. Primary data are described in references (Collinge et al. 1995, 1996; Hill et al. 1997; Wadsworth et al. 2004, 2008).