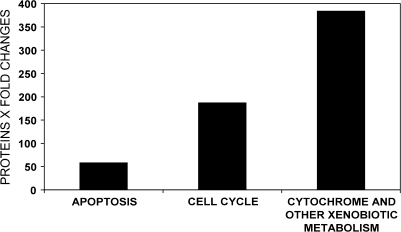
FIG. 2.
Comparison of PB protein changes as assigned to three possible nongenotoxic mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis suggested by hypothesis-driven GO modeling. Differentially expressed proteins were scored as either agonistic (+ 1), antagonistic (− 1), or no effect (0) for carcinogenesis based on the function of the protein. These scores were then multiplied by the proportional increase or decrease after PB exposure (fold change) to derive a collective quantitative value that represents both the number of proteins associated with each hypothesis and the magnitude of their changes after PB exposure.