Figure 7.
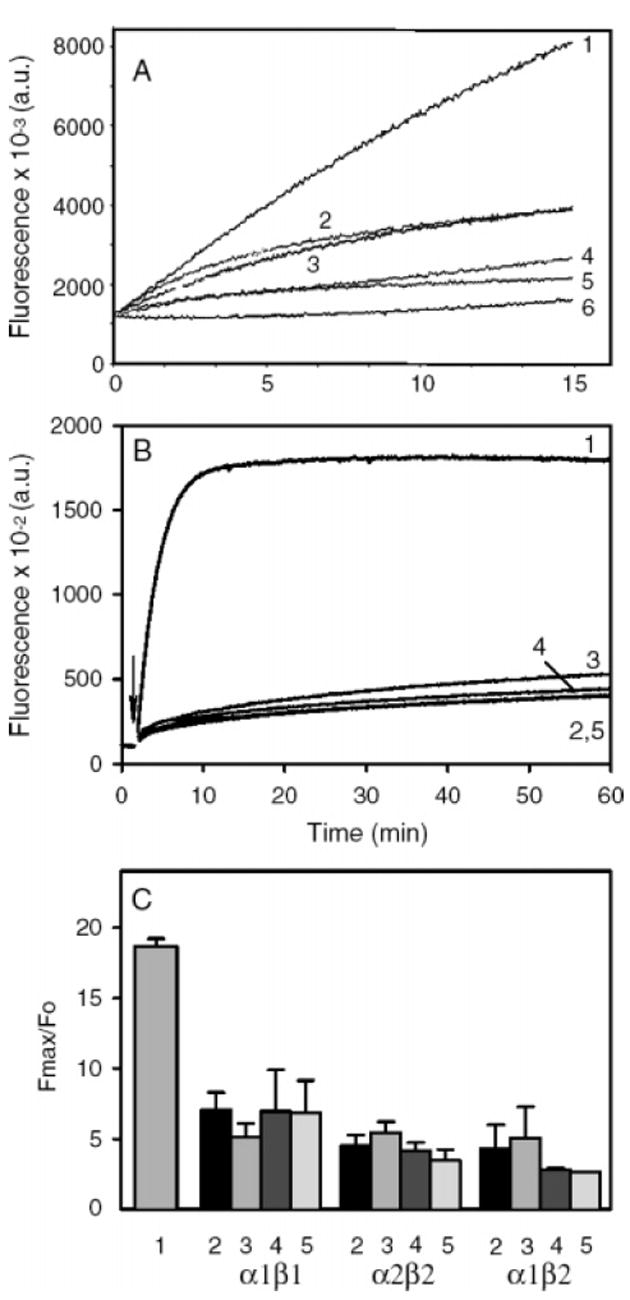
Tropomyosin does not unblock filaments with capping protein at the barbed end. (A) Spectrin-actin seeds were used to nucleate polymerization of pyrene-labeled monomeric actin (5% labeled). The seeds were prepared as previously described (15, 78), by incubating spectrin-actin with F-actin overnight to give F-actin seeds ~200 actins long, capped at their pointed ends by spectrin (1.7 nM spectrin-actin seeds and 0.5 μM F-actin). stTM was added to the F-actin to 2 μM before addition of the spectrin-actin and incubated overnight. The capping protein (α1β2) was added to the filaments just prior to the initiation of polymerization. The F-actin seeds were diluted 1:10 into Mg-G-actin (2 μM, 5% pyrene labeled) to seed polymerization in 100 mM KCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 10 Mm TrisHCl at pH 7.5, 0.2 mM ATP, 0.5 mM DTT, 0.2 mM CaCl2, and 1 mM EGTA. When present, tropomyosin concentration was 2 μM to ensure saturation of any polymer formed. Curves: 1, F-actin seeds; 2, F-actin seeds and 1.5 nM CP; 3, F-actin seeds, stTM, and 1.5 nM CP; 4, F-actin seeds and 4 nM CP; 5, F-actin seeds, stTM, and 4 nM CP; 6, G-actin alone. (B, C) Elongation experiments were carried out as described in Figures 1 and 2, and Experimental Procedures, at a final concentration of 1.5 nM CP. (B) Data from a representative data set with CPα2β2: 1, actin alone; 2, CP and no tropomyosin; 3, CP + TM5a; 4, CP + TM2; 5, CP + stTM. (C) Fmax (at 60 min) relative to the initial fluorescence (Fo) for actin alone, and the three capping proteins with the three tropomyosin isoforms, mean with standard error for 3 experiments with CP alone and TM5a, two to three experiments with TM2, and one to two experiments with stTM. The numbering corresponds to that in B.
